Cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) MRI with CO2 challenge: A technical review
- PMID: 29574034
- PMCID: PMC6150860
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.03.047
Cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) MRI with CO2 challenge: A technical review
Abstract
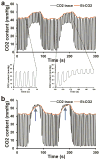
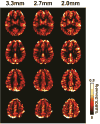
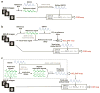
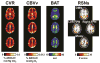
Cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) is an indicator of cerebrovascular reserve and provides important information about vascular health in a range of brain conditions and diseases. Unlike steady-state vascular parameters, such as cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral blood volume (CBV), CVR measures the ability of cerebral vessels to dilate or constrict in response to challenges or maneuvers. Therefore, CVR mapping requires a physiological challenge while monitoring the corresponding hemodynamic changes in the brain. The present review primarily focuses on methods that use CO2 inhalation as a physiological challenge while monitoring changes in hemodynamic MRI signals. CO2 inhalation has been increasingly used in CVR mapping in recent literature due to its potency in causing vasodilation, rapid onset and cessation of the effect, as well as advances in MRI-compatible gas delivery apparatus. In this review, we first discuss the physiological basis of CVR mapping using CO2 inhalation. We then review the methodological aspects of CVR mapping, including gas delivery apparatus, the timing paradigm of the breathing challenge, the MRI imaging sequence, and data analysis. In addition, we review alternative approaches for CVR mapping that do not require CO2 inhalation.
Keywords: Arterial spin labeling; BOLD; Carbon dioxide; Cerebrovascular reactivity; Cerebrovascular reserve; End-tidal CO2; Hypercapnia; Phase-contrast MRI.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Askrog V. Changes in (a-A)CO2 difference and pulmonary artery pressure in anesthetized man. J Appl Physiol. 1966;21:1299–1305. - PubMed
-
- Bhavani-Shankar K, Kumar AY, Moseley HS, Ahyee-Hallsworth R. Terminology and the current limitations of time capnography: a brief review. J Clin Monit. 1995;11:175–182. - PubMed
-
- Bhogal AA, Philippens ME, Siero JC, Fisher JA, Petersen ET, Luijten PR, Hoogduin H. Examining the regional and cerebral depth-dependent BOLD cerebrovascular reactivity response at 7T. Neuroimage. 2015;114:239–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

