Effects of fenoldopam on kidney function parameters and its therapeutic efficacy in the management of acute kidney injury in dogs with heatstroke
- PMID: 29575360
- PMCID: PMC5980265
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.15081
Effects of fenoldopam on kidney function parameters and its therapeutic efficacy in the management of acute kidney injury in dogs with heatstroke
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is common in dogs, but evidence of efficacy of its treatment is lacking.
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of fenoldopam in the management of AKI.
Animals: Forty dogs with naturally occurring heatstroke.
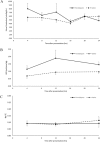
Methods: Dogs were prospectively enrolled and divided into treatment and the placebo groups (fenoldopam, constant rate infusion [CRI] of 0.1 µg/kg/min or saline, respectively). Urine production (UP) was measured using a closed system. Urinary clearances were performed at 4, 12, and 24 hours after presentation to estimate the effect of fenoldopam on UP, glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and sodium fractional excretion (NaFE).
Results: At presentation, severity of heatstroke, based on a previously developed scoring system, was similar between the study groups, but was significantly worse in nonsurvivors compared with survivors. Fenoldopam administration was not associated with hypotension. Overt AKI was diagnosed, based on the International Renal Interest Society guidelines in 22/40 (55%) of the dogs. Overall, 14/40 dogs (35%) died, with no significant (P = .507) mortality rate difference between the fenoldopam (6/20 dogs; 30%) and placebo (8/20; 40%) groups. The proportion of dogs with AKI did not differ between the fenoldopam and the placebo groups (9/20; 45% versus 13/20; 65%, respectively; P = .204). There were no differences in UP, GFR, and NaFE between the fenoldopam and the placebo groups.
Conclusion and clinical importance: Fenoldopam CRI at 0.1 µg/kg/min did not have a clinically relevant effect on kidney function parameters in dogs with severe heatstroke-associated AKI.
Keywords: acute renal failure; canine; dopamine; hypotension; renal.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Behrend EN, Grauer GF, Mani I, Groman RP, Salman MD, Greco DS. Hospital‐acquired acute renal failure in dogs: 29 cases (1983–1992). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1996;208:537–541. - PubMed
-
- Vaden SL, Levine J, Breitschwerdt EB. A retrospective case‐control of acute renal failure in 99 dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 1997;11:58–64. - PubMed
-
- Adin CA, Cowgill LD. Treatment and outcome of dogs with leptospirosis: 36 cases (1990–1998). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2000;216:371–375. - PubMed
-
- Brown SA, Barsanti JA, Crowell WA. Gentamicin‐associated acute renal failure in the dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1985;186:686–690. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

