Cross-sectional survey of biosimilar insulin utilization in Asia: The Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation Program
- PMID: 29575724
- PMCID: PMC6215931
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12843
Cross-sectional survey of biosimilar insulin utilization in Asia: The Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation Program
Abstract
Aims/introduction: Biosimilar insulin can reduce treatment costs, although the extent of its use is largely unknown. We examined biosimilar insulin use and its associations with the quality of glycemic control using the Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation register.
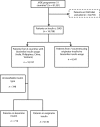
Materials and methods: We carried out a cross-sectional analysis in 81,531 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes enrolled into the Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation Program from 2007 to 2014. All insulin related terms are extracted from the Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation portal, and compared clinical profiles between biosimilar and originator insulin users. Multivariate analysis was performed to assess the association of biosimilar insulin compared with originator insulin with dosage, glycated hemoglobin and hypoglycemia events.
Results: Amongst 81,531 patients, 20.5% (n = 16,738) were insulin-treated. In four countries with high use of biosimilar insulin, 4.7% (n = 719) of insulin users (n = 10,197) were treated with biosimilar insulin (India n = 507, 70.3%; the Philippines n = 90, 12.5%; China n = 62, 8.6%; Vietnam n = 60, 8.3%). Biosimilar insulin users were younger and had higher body mass index, glycated hemoglobin, insulin dosage and more frequent hypoglycemia than originator insulin users. These associations were non-significant after adjustment for confounders. Only age, college education, diabetes education, lipid control, physical activity and history of cardiovascular complications were independently associated with these quality measures.
Conclusions: Biosimilar insulin use is not uncommon in Asia. Data exclusion due to incomplete capturing of brand names suggests possibly higher use. The multiple determinants of the quality of glycemic control call for establishment of prospective cohorts and diabetes registers to monitor the safety and efficacy of different brands of biosimilar insulin and their impacts on clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Asia; Biosimilar; Insulin.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- IDF . IDF Diabetes Atlas. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation, 2012.
-
- Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, et al Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA 2009; 301: 2129–2140. - PubMed
-
- Chuang LM, Tsai ST, Huang BY, et al The status of diabetes control in Asia–a cross‐sectional survey of 24 317 patients with diabetes mellitus in 1998. Diabet Med 2002; 19: 978–985. - PubMed
-
- Administration USFDA . Guidance for Industry: Quality Considerations in Demonstrating Biosimilarity to a Reference Protein Product. Rockville, MD: FDA, 2012. Available from: https://wwwfdagov/downloads/drugs/guidances/ucm291134pdf. Accessed October 1, 2017.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous