Combination therapy of apatinib with icotinib for primary acquired icotinib resistance in patients with advanced pulmonary adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutation
- PMID: 29575765
- PMCID: PMC5928351
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12624
Combination therapy of apatinib with icotinib for primary acquired icotinib resistance in patients with advanced pulmonary adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutation
Abstract
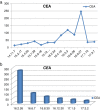
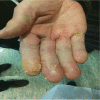
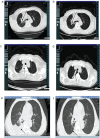
Multi-targeted agents represent the next generation of targeted therapies for solid tumors, and patients with acquired resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) may also benefit from their combination with TKI therapy. Third-generation targeted drugs, such as osimertinib, are very expensive, thus a more economical solution is required. The aim of this study was to explore the use of apatinib combined with icotinib therapy for primary acquired resistance to icotinib in three patients with advanced pulmonary adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. We achieved favorable oncologic outcomes in all three patients, with progression-free survival of four to six months. Unfortunately, the patients ultimately had to cease combination therapy because of intolerable adverse effects of hand and foot syndrome and oral ulcers. Combination therapy of apatinib with icotinib for primary acquired resistance to icotinib may be an option for patients with advanced pulmonary adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations, but physicians must also be aware of the side effects caused by such therapy.
Keywords: Acquired resistance; advanced pulmonary adenocarcinoma; apatinib; icotinib; molecular targeted therapy.
© 2018 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes of concurrent versus sequential icotinib therapy and chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR mutations.Clin Transl Sci. 2021 May;14(3):890-897. doi: 10.1111/cts.12951. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Clin Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 33382908 Free PMC article.
-
Positive response to Icotinib in metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with acquiring EGFR Leu792H mutation after AZD9291 treatment: a case report.BMC Cancer. 2019 Feb 8;19(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5352-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30736738 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation of advanced lung adenocarcinoma to acquired T790M resistance mutation adenosquamous carcinoma following tyrosine kinase inhibitor: a case report.Tumori. 2021 Dec;107(6):NP5-NP10. doi: 10.1177/0300891620973262. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Tumori. 2021. PMID: 33896242
-
Combination of icotinib and chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced lung adenocarcinoma in patients with sensitive EGFR mutations: A randomized controlled study.Lung Cancer. 2019 Jul;133:23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 May 7. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31200823 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of EGFR-TKIs in a Patient with Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring an EGFR-RAD51 Fusion.Oncologist. 2019 Aug;24(8):1027-1030. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0732. Epub 2019 May 7. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 31064887 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 134 (Published erratum appears in) CA Cancer J Clin 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Wu YL, Zhong WZ, Li LY et al Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and their correlation with gefitinib therapy in patients with non‐small cell lung cancer: A meta‐analysis based on updated individual patient data from six medical centers in mainland China. J Thorac Oncol 2007; 2: 430–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

