Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 overexpression promotes lymph node micrometastasis in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 29575778
- PMCID: PMC5928384
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12598
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 overexpression promotes lymph node micrometastasis in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is constitutively activated in several malignancies. Here, we define the correlation between STAT3 expression and lymph node micrometastasis of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Then we highlight some possibilities associated with developing a way to detect tumor micrometastasis and an anticancer drug that might therapeutically inhibit the STAT3 signaling pathway.
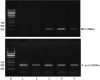
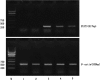
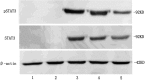
Methods: The samples were collected from 50 patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and 50 patients with benign lung tumors. Mucin 1 mRNA expression was evaluated to determine lymph node micrometastasis status. STAT3 mRNA, STAT3 protein, and phosphorylated STAT3 protein expression were evaluated through reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, western blot, and immunohistochemistry, respectively. Measurement data was represented as mean ± standard deviation, and the t-rest or F-test were used. The χ2 -test was used in enumeration data. Logistic regression analysis was carried out to determine the independent risk factors influencing lymph node micrometastasis.
Results: STAT3 mRNA and proteins expression were correlated with lymph node micrometastasis (P < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis revealed STAT3 protein overexpression and the differentiation degree of tumors were independent risk factors for lymph node micrometastasis.
Conclusion: Overexpression of STAT3 might promote lymphatic micrometastasis of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and might be a clinical predictor of lymph node micrometastasis.
Keywords: Lymph node micrometastasis; mucin 1; non-small cell lung cancer; phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
© 2018 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gene diagnosis of micrometastases in regional lymph nodes of patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer: impact on staging and prognosis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2013 Nov;15(11):882-8. doi: 10.1007/s12094-013-1017-1. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Clin Transl Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23404657
-
Clinical significance of detecting mucin 1 mRNA in diagnosing occult lymph node micrometastasis in esophageal cancer patients.Ai Zheng. 2007 Feb;26(2):194-9. Ai Zheng. 2007. PMID: 17298752
-
Molecular diagnosis and prognostic significance of lymph node micrometastasis in patients with histologically node-negative non-small cell lung cancer.Tumour Biol. 2013 Apr;34(2):1245-53. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0667-5. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23355336
-
Lymph node micrometastasis in non-small cell lung cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 May;149:112817. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112817. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35303567 Review.
-
A meta-analysis of STAT3 and phospho-STAT3 expression and survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014 Mar;40(3):311-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2013.11.012. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24332948 Review.
Cited by
-
Positive relationship between number of negative lymph nodes and duration of gallbladder cancer cause-specific survival after surgery.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Dec 13;10:6961-6969. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S187857. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30588101 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-11: A Potential Biomarker and Molecular Therapeutic Target in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cells. 2022 Jul 21;11(14):2257. doi: 10.3390/cells11142257. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35883698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine Learning for the Prediction of Lymph Nodes Micrometastasis in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comparative Analysis of Two Practical Prediction Models for Gross Target Volume Delineation.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Jun 17;13:4811-4820. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S313941. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34168500 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNA-590-5p functions as a liquid biopsy marker in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2020 Mar;111(3):826-839. doi: 10.1111/cas.14199. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31520555 Free PMC article.
-
Lymph node dissection of station 8 improves the survival of T≤3 cmN0M0 lung adenocarcinoma patients.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 30;13(7):1530-1543. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-184. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39118884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2013; 63: 11–30. - PubMed
-
- Araki K, Kidokoro Y, Hosoya K et al Excellent prognosis of lepidic‐predominant lung adenocarcinoma: Low incidence of lymphatic vessel invasion as a key factor. Anticancer Res 2014; 34: 3153–6. - PubMed
-
- Balic M, Williams A, Dandachi N, Cote RJ. Micrometastasis: Detection methods and clinical importance. Cancer Biomark 2011; 9: 397–419. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

