The essential function of CARD9 in diet-induced inflammation and metabolic disorders in mice
- PMID: 29575791
- PMCID: PMC5980191
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13494
The essential function of CARD9 in diet-induced inflammation and metabolic disorders in mice
Abstract
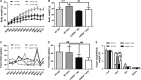
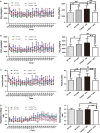
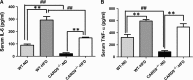
Inflammation and metabolic disorder are common pathophysiological conditions, which play a vital role in the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes. The purpose of this study was to explore the effects of caspase recruitment domain (CARD) 9 in the high fat diet (HFD)-treated mice and attempt to find a molecular therapeutic target for obesity development and treatment. Sixteen male CARD9-/- and corresponding male WT mice were fed with normal diet or high fat diet, respectively, for 12 weeks. Glucose tolerance, insulin resistance, oxygen consumption and heat production of the mice were detected. The CARD9/MAPK pathway-related gene and protein were determined in insulin-responsive organs using Western blotting and quantitative PCR. The results showed that HFD-induced insulin resistance and impairment of glucose tolerance were more severe in WT mice than that in the CARD9-/- mice. CARD9 absence significantly modified O2 consumption, CO2 production and heat production. CARD9-/- mice displayed the lower expression of p38 MAPK, JNK and ERK when compared to the WT mice in both HFD- and ND-treated groups. HFD induced the increase of p38 MAPK, JNK and ERK in WT mice but not in the CARD9-/- mice. The results indicated that CARD9 absence could be a vital protective factor in diet-induced obesity via the CARD9/MAPK pathway, which may provide new insights into the development of gene knockout to improving diet-induced obesity and metabolism disorder.
Keywords: CARD9; energy metabolism obesity; inflammation; insulin resistance.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CARD9 knockout ameliorates myocardial dysfunction associated with high fat diet-induced obesity.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Mar;92:185-95. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.02.014. Epub 2016 Feb 17. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26900039 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc rescues obesity-induced cardiac hypertrophy via stimulating metallothionein to suppress oxidative stress-activated BCL10/CARD9/p38 MAPK pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Jun;21(6):1182-1192. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13050. Epub 2017 Feb 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28158919 Free PMC article.
-
Exacerbation by knocking-out metallothionein gene of obesity-induced cardiac remodeling is associated with the activation of CARD9 signaling.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jan 13;21(3):1032-1046. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.105513. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39897024 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc homeostasis plays an important role in the prevention of obesity-induced cardiac inflammation, remodeling and dysfunction.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020 Dec;62:126615. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126615. Epub 2020 Jul 10. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32683230 Review.
-
The Role of CARD9 in Metabolic Diseases.Curr Med Sci. 2020 Apr;40(2):199-205. doi: 10.1007/s11596-020-2166-4. Epub 2020 Apr 26. Curr Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32337681 Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling pathways in obesity: mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 28;7(1):298. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01149-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36031641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CARD9 deficiency improves the recovery of limb ischemia in mice with ambient fine particulate matter exposure.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 13;10:1125717. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1125717. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36860276 Free PMC article.
-
The signaling pathways in obesity-related complications.J Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jun 7;18(2):e12039. doi: 10.1002/ccs3.12039. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38946722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CARD9 mediates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;192:114670. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114670. Epub 2021 Jul 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34233162 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of white adipose tissue metabolic dysfunction in obesity: mechanisms and opportunities.MedComm (2020). 2024 May 24;5(6):e560. doi: 10.1002/mco2.560. eCollection 2024 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38812572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bertin J, Guo Y, Wang L, et al CARD9 is a novel caspase recruitment domain‐containing protein that interacts with BCL10/CLAP and activates NF‐kappa B. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275: 41082–6. - PubMed
-
- Hara H, Ishihara C, Takeuchi A, et al The adaptor protein CARD9 is essential for the activation of myeloid cells through ITAM‐associated and Toll‐like receptors. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8: 619–29. - PubMed
-
- Gross O, Gewies A, Finger K, et al Card9 controls a non‐TLR signalling pathway for innate anti‐fungal immunity. Nature. 2006; 442: 651–6. - PubMed
-
- Hsu YM, Zhang Y, You Y, et al The adaptor protein CARD9 is required for innate immune responses to intracellular pathogens. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8: 198–205. - PubMed
-
- LeibundGut‐Landmann S, Gross O, Robinson MJ, et al Syk‐ and CARD9‐dependent coupling of innate immunity to the induction of T helper cells that produce interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8: 630–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

