Armed oncolytic viruses: A kick-start for anti-tumor immunity
- PMID: 29576283
- PMCID: PMC7108398
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2018.03.006
Armed oncolytic viruses: A kick-start for anti-tumor immunity
Abstract
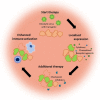
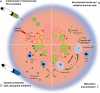
Oncolytic viruses (OVs), viruses that specifically result in killing tumor cells, represent a promising class of cancer therapy. Recently, the focus in the OV therapy field has shifted from their direct oncolytic effect to their immune stimulatory effect. OV therapy can function as a "kick start" for the antitumor immune response by releasing tumor associated antigens and release of inflammatory signals. Combining OVs with immune modulators could enhance the efficacy of both immune and OV therapies. Additionally, genetic engineering of OVs allows local expression of immune therapeutics, thereby reducing related toxicities. Different options to modify the tumor microenvironment in combination with OV therapy have been explored. The possibilities and obstacles of these combinations will be discussed in this review.
Keywords: Immune therapy; Oncolytic viruses; Transgenes.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Dunn G.P., Bruce A.T., Ikeda H., Old L.J., Schreiber R.D. Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3(no. 11):991–998. - PubMed
-
- Chen D.S., Mellman I. Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-Immunity cycle. Immunity. 2013;39(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Kapsenberg M.L. Dendritic-cell control of pathogen-driven T-cell polarization. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3(no. 12):984–993. - PubMed
-
- Waldhauer I., Steinle A. NK cells and cancer immunosurveillance. Oncogene. 2008;27(no. 45):5932–5943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

