Lung Epithelial Cells Coordinate Innate Lymphocytes and Immunity against Pulmonary Fungal Infection
- PMID: 29576482
- PMCID: PMC5951304
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.02.011
Lung Epithelial Cells Coordinate Innate Lymphocytes and Immunity against Pulmonary Fungal Infection
Erratum in
-
Lung Epithelial Cells Coordinate Innate Lymphocytes and Immunity against Pulmonary Fungal Infection.Cell Host Microbe. 2019 Apr 10;25(4):630. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.03.013. Cell Host Microbe. 2019. PMID: 30974087 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Lung epithelial cells (LECs) are strategically positioned in the airway mucosa to provide barrier defense. LECs also express pattern recognition receptors and a myriad of immune genes, but their role in immunity is often concealed by the activities of "professional" immune cells, particularly in the context of fungal infection. Here, we demonstrate that NF-κB signaling in LECs is essential for immunity against the pulmonary fungal pathogen Blastomyces dermatitidis. LECs orchestrate innate antifungal immunity by augmenting the numbers of interleukin-17A (IL-17A)- and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)-producing innate lymphocytes, specifically "natural" Th17 (nTh17) cells. Innate lymphocyte-derived IL-17A and GM-CSF in turn enable phagocyte-driven fungal killing. LECs regulate the numbers of nTh17 cells via the production of chemokines such as CCL20, a process dependent on IL-1α-IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) signaling on LECs. Therefore, LECs orchestrate IL-17A- and GM-CSF-mediated immunity in an IL-1R-dependent manner and represent an essential component of innate immunity to pulmonary fungal pathogens.
Keywords: epithelial cells; fungi; innate immunity; lymphocytes.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
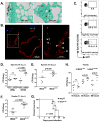


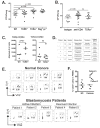

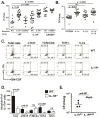
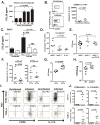
References
-
- Aimanianda V, Bayry J, Bozza S, Kniemeyer O, Perruccio K, Elluru SR, Clavaud C, Paris S, Brakhage AA, Kaveri SV, et al. Surface hydrophobin prevents immune recognition of airborne fungal spores. Nature. 2009;460:1117–1121. - PubMed
-
- Balbi B, Valle MT, Oddera S, Giunti D, Manca F, Rossi GA, Allegra L. T-lymphocytes with gamma delta+ V delta 2+ antigen receptors are present in increased proportions in a fraction of patients with tuberculosis or with sarcoidosis. The American review of respiratory disease. 1993;148:1685–1690. - PubMed
-
- Bar E, Whitney PG, Moor K, Reis ESC, Leibundgut-Landmann S. IL-17 Regulates Systemic Fungal Immunity by Controlling the Functional Competence of NK Cells. Immunity 2014 - PubMed
-
- Carding SR, Egan PJ. Gammadelta T cells: functional plasticity and heterogeneity. Nature reviews Immunology. 2002;2:336–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

