Capsaicin reverses the inhibitory effect of licochalcone A/β-Arbutin on tyrosinase expression in b16 mouse melanoma cells
- PMID: 29576710
- PMCID: PMC5858230
- DOI: 10.4103/pm.pm_103_17
Capsaicin reverses the inhibitory effect of licochalcone A/β-Arbutin on tyrosinase expression in b16 mouse melanoma cells
Abstract
Introduction: Melanin is synthesized by melanocytes, which are located in the basal layer of the skin. After synthesis, melanin is further deposited on the surface of the skin to form black spots or chloasma. Tyrosinase is a rate-limiting enzyme that plays an important role in melanogenesis. Currently, there are many drugs that inhibit tyrosinase expression to further reduce melanogenesis. Nevertheless, some of these could reverse the pharmacological effect of other drugs, when used simultaneously.
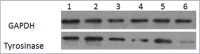
Materials and methods: B16 mouse melanoma cells were treated with the tyrosinase inhibitors licochalcone A and β-arbutin, alone or in combination with capsaicin, an alkaloid found in peppers. Cytotoxicity, melanin content, and tyrosinase activity and expression were determined.
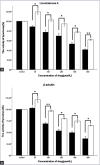
Results: Licochalcone A/β-arbutin inhibited tyrosinase expression and further hindered melanin synthesis when applied individually to B16 mouse melanoma cells. However, licochalcone A/β-arbutin combined with 50 μmol/L capsaicin enhanced the expression of tyrosinase in these cells and further increased melanin content.
Conclusion: Our data implied that capsaicin could reverse the inhibitory effect of licochalcone A/β-arbutin on tyrosinase expression in B16 mouse melanoma cells.
Summary: B16 mouse melanoma cells were treated with the tyrosinase inhibitors licochalcone A and β-arbutin, alone or in combination with capsaicin, an alkaloid found in peppers. Cytotoxicity, melanin content, and tyrosinase activity and expression were determined. Licochalcone A/β-arbutin inhibited tyrosinase expression and further hindered melanin synthesis when applied individually to B16 mouse melanoma cells. However, licochalcone A/β-arbutin combined with 50 μmol/L capsaicin enhanced the expression of tyrosinase in these cells and further increased melanin content. Our research implied that capsaicin could reverse the inhibitory effect of licochalcone A/β-arbutin on tyrosinase expression in B16 mouse melanoma cells. Abbreviations used: B16: B16 mouse melanoma cells; L-DOPA: 3, 4-L-dihydroxyphenylalanine; TYR: Tyrosinase; USP: United States Pharmacopeia; FBS: Fetal bovine serum; EDTA: Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; RPMI: Roswell Park Memorial Institute; MTT3: 4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide, NaOH: Sodium hydroxide; PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline; RIPA: Radio-immunoprecipitation assay; PMSF: Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride or phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride; SDS: Sodium dodecyl sulfate, sodium salt; PVDF: Polyvinylidene fluoride; ECL: Enhanced chemiluminescence.
Keywords: Capsaicin; licochalcone A; melanin; melanocyte; tyrosinase; β-arbutin.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Inhibitory effect of arbutin on melanogenesis--biochemical study using cultured B16 melanoma cells].Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1991 May;101(6):609-13. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1991. PMID: 1920891 Japanese.
-
Ethyl acetate extract from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer and its main constituents inhibit α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced melanogenesis by suppressing oxidative stress in B16 mouse melanoma cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Aug 17;208:149-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28689798
-
Assessment of Cuscuta chinensis seeds׳ effect on melanogenesis: comparison of water and ethanol fractions in vitro and in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 May 28;154(1):240-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.04.016. Epub 2014 Apr 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24746484
-
Diethylstilbestrol enhances melanogenesis via cAMP-PKA-mediating up-regulation of tyrosinase and MITF in mouse B16 melanoma cells.Steroids. 2011 Nov;76(12):1297-304. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2011.06.008. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Steroids. 2011. PMID: 21745488
-
Recent Progress on Feasible Strategies for Arbutin Production.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 May 9;10:914280. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.914280. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35615473 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Application Potential of a Recombinant Ganoderma Protein as Bioactive Ingredients in Cosmetics.Molecules. 2023 Apr 6;28(7):3272. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073272. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37050035 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Arbutin on The Expression of Tumor Suppressor P53, BAX/BCL-2 Ratio and Oxidative Stress Induced by Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide in Fibroblast and LNcap Cell Lines.Cell J. 2021 Jan;22(4):532-541. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2021.6902. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Cell J. 2021. PMID: 32347047 Free PMC article.
-
Arbutin as a Skin Depigmenting Agent with Antimelanogenic and Antioxidant Properties.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jul 15;10(7):1129. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071129. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technologies for Solubility, Dissolution and Permeation Enhancement of Natural Compounds.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 May 25;15(6):653. doi: 10.3390/ph15060653. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35745572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemicals as Immunomodulatory Agents in Melanoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 31;24(3):2657. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032657. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ito S, Wakamatsu K. Chemistry of mixed melanogenesis – Pivotal roles of dopaquinone. Photochem Photobiol. 2008;84:582–92. - PubMed
-
- Ramsden CA, Riley PA. Tyrosinase: The four oxidation states of the active site and their relevance to enzymatic activation, oxidation and inactivation. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014;22:2388–95. - PubMed
-
- Sturm RA, Teasdale RD, Box NF. Human pigmentation genes: Identification, structure and consequences of polymorphic variation. Gene. 2001;277:49–62. - PubMed
-
- Tripathi RK, Hearing VJ, Urabe K, Aroca P, Spritz RA. Mutational mapping of the catalytic activities of human tyrosinase. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:23707–12. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Wang J, Zhou W, Wang Y, Yang L. Systems approaches and polypharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines: An example using licorice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;146:773–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
