Cordyceps militaris Fraction induces apoptosis and G2/M Arrest via c-Jun N-Terminal kinase signaling pathway in oral squamous carcinoma KB Cells
- PMID: 29576711
- PMCID: PMC5858231
- DOI: 10.4103/pm.pm_63_17
Cordyceps militaris Fraction induces apoptosis and G2/M Arrest via c-Jun N-Terminal kinase signaling pathway in oral squamous carcinoma KB Cells
Abstract
Background: Cordyceps militaris fraction (CMF) has been shown to possess in vitro antitumor activity against human chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells in our previous research.
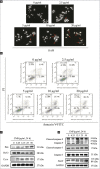
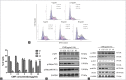
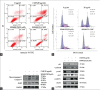
Materials and methods: The in vitro inhibitory activities of CMF on the growth of KB cells were evaluated by viability assay. The apoptotic and cell cycle influences of CMF were detected by 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining and flow cytometry assay. The expression of different apoptosis-associated proteins and cell cycle regulatory proteins was examined by Western blot assay. The nuclear localization of c-Jun was observed by fluorescence staining.
Objective: The objective of this study was to investigate the antiproliferative effect of CMF as well as the mechanism underlying the apoptosis and cell cycle arrest it induces in KB cells.
Results: CMF suppressed KB cells' proliferation in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Flow cytometric analysis indicated that CMF induced G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Western blot analysis revealed that CMF induced caspase-3, caspase-9, and PARP cleavages, and increased the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. CMF also led to increased expression of p21, decreased expression of cyclin B1, mitotic phosphatase cdc25c, and mitotic kinase cdc2, as well as unchanged expression of p53. In addition, CMF stimulated c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) protein phosphorylations, resulting in upregulated expression of c-Jun and nuclear localization of c-Jun. Pretreatment with JNK inhibitor SP600125 suppressed CMF-induced apoptosis and G2/M arrest.
Conclusions: CMF is capable of modulating c-Jun caspase and Bcl-2 family proteins through JNK-dependent apoptosis, which results in G2/M phase arrest in KB cells. CMF could be developed as a promising candidate for the new antitumor agents.
Summary: CMF exhibited strong anticancer activity against oral squamous carcinoma KB cellsCMF inhibited KB cells' proliferation via induction of apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrestCMF activated JNK signaling pathway and promoted the nuclear localization of c-JunCMF regulated the apoptosis- and cell cycle-related proteins in a manner dependent on JNK/c-Jun pathway. Abbreviations used: CMF: Cordyceps militaris fraction; OSCC: Oral squamous cell carcinoma; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cordyceps militaris fraction; KB cells; c-Jun N-terminal kinases/c-Jun; cell cycle arrest.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Romidepsin induces G2/M phase arrest via Erk/cdc25C/cdc2/cyclinB pathway and apoptosis induction through JNK/c-Jun/caspase3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2017 Mar 1;127:90-100. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28012958
-
Induction of apoptosis by Cordyceps militaris fraction in human chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells involved with mitochondrial dysfunction.Pharmacogn Mag. 2014 Jul;10(39):325-31. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.137374. Pharmacogn Mag. 2014. PMID: 25210321 Free PMC article.
-
Longikaurin A, a natural ent-kaurane, induces G2/M phase arrest via downregulation of Skp2 and apoptosis induction through ROS/JNK/c-Jun pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Mar 20;5(3):e1137. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.66. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24651440 Free PMC article.
-
Se-Enriched Cordyceps militaris Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Induces Cell Apoptosis, And Causes G2/M Phase Arrest In Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Oct 23;12:8751-8763. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S217017. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31749621 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Complex Apoptotic Signaling Pathways on Cancer Cell Sensitivity to Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 28;16(5):984. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050984. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473345 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Baicalin modulates apoptosis via RAGE, MAPK, and AP-1 in vascular endothelial cells during Haemophilus parasuis invasion.Innate Immun. 2019 Oct;25(7):420-432. doi: 10.1177/1753425919856078. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Innate Immun. 2019. PMID: 31271085 Free PMC article.
-
Cordyceps militaris-Derived Bioactive Gels: Therapeutic and Anti-Aging Applications in Dermatology.Gels. 2025 Jan 3;11(1):33. doi: 10.3390/gels11010033. Gels. 2025. PMID: 39852004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of lncRNA ANRIL silencing on anoikis and cell cycle in human glioma via microRNA-203a.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Aug 23;11:5103-5109. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S169809. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30197521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Sun C, He S, Guo X, Xu H, Zeng X, et al. Apoptotic effects of diosgeninlactoside on oral squamous carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37:1450–9. - PubMed
-
- Yoshikawa N, Nakamura K, Yamaguchi Y, Kagota S, Shinozuka K, Kunitomo M. Antitumour activity of cordycepin in mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2004;31(Suppl 2):S51–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
