MRI detection of bacterial brain abscesses and monitoring of antibiotic treatment using bacCEST
- PMID: 29577382
- PMCID: PMC5910221
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27180
MRI detection of bacterial brain abscesses and monitoring of antibiotic treatment using bacCEST
Abstract
Purpose: To develop a new MRI method to detect and characterize brain abscesses using the CEST contrast inherently carried by bacterial cells, namely bacCEST.
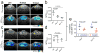
Methods: Bacteria S. aureus (ATCC #49775) and F98 and 9L glioma cells were injected stereotactically in the brains of F344 rats to form abscesses and tumors. The CEST signals of brain abscesses (n = 4) and tumors (n = 7) were acquired using 2 B1 values (i.e., 1 and 3 µT) and compared. The bacCEST signal of the brain abscesses in the rats (n = 3) receiving ampicillin (intraperitoneal injection 40 mg/kg twice daily) was acquired before, 4 and 10 days after the treatment.
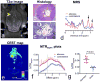
Results: The bacCEST signal of S. aureus was characterized in vitro as a strong and broad signal in the range of 1 to 4 ppm, with the maximum contrast occurring at 2.6 ppm. The CEST signal in S. aureus-induced brain abscesses was significantly higher than that of contralateral parenchyma (p = .003). Moreover, thanks to their different B1 independence, brain abscesses and tumors could be effectively differentiated (p = .005) using ΔCEST(2.6 ppm, 3 µT-1 µT), defined by the difference between the CEST signal (offset = 2.6 ppm) acquired using B1 = 3 µT and that of 1 µT. In treated rats, bacCEST MRI could detect the response of bacteria as early as 4 days after the antibiotic treatment (p = .035).
Conclusion: BacCEST MRI provides a new imaging method to detect, discriminate, and monitor bacterial infection in deep-seated organs. Because no contrast agent is needed, such an approach has a great translational potential for detecting and monitoring bacterial infection in deep-seated organs.
Keywords: CEST; MRI; bacterial infection; brain abscess.
© 2018 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Brouwer MC, van de Beek D. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of brain abscesses. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017;30(1):129–134. - PubMed
-
- Brouwer MC, Tunkel AR, McKhann GM, 2nd, van de Beek D. Brain abscess. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(5):447–456. - PubMed
-
- Takeshita M, Kagawa M, Izawa M, Takakura K. Current treatment strategies and factors influencing outcome in patients with bacterial brain abscess. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1998;140(12):1263–1270. - PubMed
-
- Seydoux C, Francioli P. Bacterial brain abscesses: factors influencing mortality and sequelae. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;15(3):394–401. - PubMed
-
- Yang SY, Zhao CS. Review of 140 patients with brain abscess. Surg Neurol. 1993;39(4):290–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

