Neutrophil-Based Drug Delivery Systems
- PMID: 29577477
- PMCID: PMC6161715
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.201706245
Neutrophil-Based Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
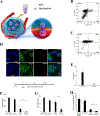
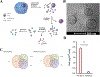
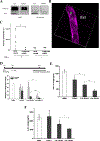
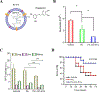
White blood cells (WBCs) are a major component of immunity in response to pathogen invasion. Neutrophils are the most abundant WBCs in humans, playing a central role in acute inflammation induced by pathogens. Adhesion to vasculature and tissue infiltration of neutrophils are key processes in acute inflammation. Many inflammatory/autoimmune disorders and cancer therapies have been found to be involved in activation and tissue infiltration of neutrophils. A promising strategy to develop novel targeted drug delivery systems is the targeting and exploitation of activated neutrophils. Herein, a new drug delivery platform based on neutrophils is reviewed. There are two types of drug delivery systems: neutrophils as carriers and neutrophil-membrane-derived nanovesicles. It is discussed how nanoparticles hijack neutrophils in vivo to deliver therapeutics across blood vessel barriers and how neutrophil-membrane-derived nanovesicles target inflamed vasculature. Finally, the potential applications of neutrophil-based drug delivery systems in treating inflammation and cancers are presented.
Keywords: cancer; inflammation; nanovesicles; neutrophils; targeted drug delivery.
© 2018 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

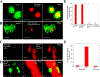
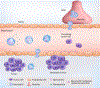
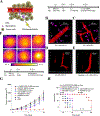
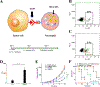

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

