Class I HDAC inhibition is a novel pathway for regulating astrocytic apoE secretion
- PMID: 29579087
- PMCID: PMC5868809
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194661
Class I HDAC inhibition is a novel pathway for regulating astrocytic apoE secretion
Abstract
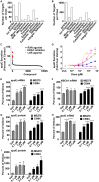
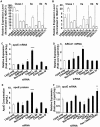
Despite the important role of apolipoprotein E (apoE) secretion from astrocytes in brain lipid metabolism and the strong association of apoE4, one of the human apoE isoforms, with sporadic and late onset forms of Alzheimer's disease (AD) little is known about the regulation of astrocytic apoE. Utilizing annotated chemical libraries and a phenotypic screening strategy that measured apoE secretion from a human astrocytoma cell line, inhibition of pan class I histone deacetylases (HDACs) was identified as a mechanism to increase apoE secretion. Knocking down select HDAC family members alone or in combination revealed that inhibition of the class I HDAC family was responsible for enhancing apoE secretion. Knocking down LXRα and LXRβ genes revealed that the increase in astrocytic apoE in response to HDAC inhibition occurred via an LXR-independent pathway. Collectively, these data suggest that pan class I HDAC inhibition is a novel pathway for regulating astrocytic apoE secretion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Huang Y, Weisgraber KH, Mucke L, Mahley RW. Apolipoprotein E: diversity of cellular origins, structural and biophysical properties, and effects in Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Neurosci. 2004;23(3):189–204. doi: 10.1385/JMN:23:3:189 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hauser PS, Narayanaswami V, Ryan RO. Apolipoprotein E: From lipid transport to neurobiology. Prog Lipid Res. 2011;50(1):62–74. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2010.09.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weisgraber KH, Mahley RW. Human apolipoprotein E: the Alzheimer’s disease connection. FASEB J. 1996;10(13):1485–94. - PubMed
-
- Hatters DM, Peters-Libeu CA, Weisgraber KH. Apolipoprotein E structure: insights into function. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31(8):445–54. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.06.008 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

