The molecular machines that traffic signaling receptors into and out of cilia
- PMID: 29579578
- PMCID: PMC5949257
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2018.03.004
The molecular machines that traffic signaling receptors into and out of cilia
Abstract
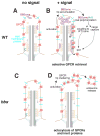
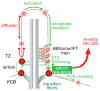
Cilia are surface-exposed organelles that dynamically concentrate signaling molecules to organize sensory, developmental and homeostatic pathways. Entry and exit of signaling receptors is germane to the processing of signals and the molecular machines for entry and exit have started to emerge. The IFT-A complex and its membrane recruitment factor Tulp3 complex promotes the entry of signaling receptors into cilia while the BBSome and its membrane recruitment factor Arl6GTP ferry activated signaling receptors out of cilia. Ciliary exit is a surprisingly complex process entailing passage through a first diffusion barrier at the transition zone, diffusion inside an intermediate compartment and crossing of a periciliary diffusion barrier. The two barriers may organize a privileged compartment where activated signaling receptors transiently reside.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Nachury MV, Loktev AV, Zhang Q, Westlake CJ, Peränen J, Merdes A, Slusarski DC, Scheller RH, Bazan JF, Sheffield VC, et al. A core complex of BBS proteins cooperates with the GTPase Rab8 to promote ciliary membrane biogenesis. Cell. 2007;129:1201–1213. - PubMed
-
- Loktev AV, Zhang Q, Beck JS, Searby CC, Scheetz TE, Bazan JF, Slusarski DC, Sheffield VC, Jackson PK, Nachury MV. A BBSome subunit links ciliogenesis, microtubule stability, and acetylation. Dev Cell. 2008;15:854–865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

