Impact of insulin signaling and proteasomal activity on physiological output of a neuronal circuit in aging Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 29579685
- PMCID: PMC5933513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.02.027
Impact of insulin signaling and proteasomal activity on physiological output of a neuronal circuit in aging Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
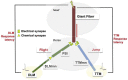
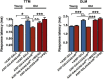
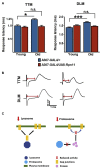
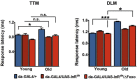
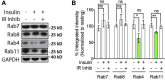
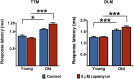
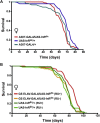
The insulin family of growth factors plays an important role in development and function of the nervous system. Reduced insulin and insulin-growth-factor signaling (IIS), however, can improve symptoms of neurodegenerative diseases in laboratory model organisms and protect against age-associated decline in neuronal function. Recently, we showed that chronic, moderately lowered IIS rescues age-related decline in neurotransmission through the Drosophila giant fiber escape response circuit. Here, we expand our initial findings by demonstrating that reduced functional output in the giant fiber system of aging flies can be prevented by increasing proteasomal activity within the circuit. Manipulations of IIS in neurons can also affect longevity, underscoring the relevance of the nervous system for aging.
Keywords: Aging; Drosophila; Gao junctions; Giant Fiber system; Insulin signaling; Proteasomal activity; Rab11; Rab4; Recycling.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Allen M.J., Drummond J.A., Moffat K.G. Development of the giant fiber neuron of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998;397:519–531. - PubMed
-
- Allen M.J., Godenschwege T.A., Tanouye M.A., Phelan P. Making an escape: development and function of the Drosophila giant fibre system. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006;17:31–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

