Mechanism of activation of the BNLF2a immune evasion gene of Epstein-Barr virus by Zta
- PMID: 29580369
- PMCID: PMC6096924
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.001056
Mechanism of activation of the BNLF2a immune evasion gene of Epstein-Barr virus by Zta
Abstract
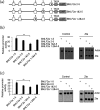
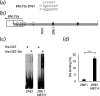
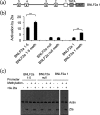
The human gamma herpes virus Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) exploits multiple routes to evade the cellular immune response. During the EBV lytic replication cycle, viral proteins are expressed that provide excellent targets for recognition by cytotoxic T cells. This is countered by the viral BNLF2a gene. In B cells during latency, where BNLF2a is not expressed, we show that its regulatory region is embedded in repressive chromatin. The expression of BNLF2a mirrors the expression of a viral lytic cycle transcriptional regulator, Zta (BZLF1, EB1, ZEBRA), in B cells and we propose that Zta plays a role in up-regulating BNLF2a. In cells undergoing EBV lytic replication, we identified two distinct regions of interaction of Zta with the chromatin-associated BNLF2a promoter. We identify five potential Zta-response elements (ZREs) in the promoter that are highly conserved between virus isolates. Zta binds to these elements in vitro and activates the expression of the BNLF2a promoter in both epithelial and B cells. We also found redundancy amongst the ZREs. The EBV genome undergoes a biphasic DNA methylation cycle during its infection cycle. One of the ZREs contains an integral CpG motif. We show that this can be DNA methylated during EBV latency and that both Zta binding and promoter activation are enhanced by its methylation. In summary, we find that the BNLF2a promoter is directly targeted by Zta and that DNA methylation within the proximal ZRE aids activation. The implications for regulation of this key viral gene during the reactivation of EBV from latency are discussed.
Keywords: BNLF2a; BZLF1; Epstein-Barr virus; epigenetics; gene expression; immune evasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analyses of Zta binding to the Epstein-Barr virus genome reveals interactions in both early and late lytic cycles and an epigenetic switch leading to an altered binding profile.J Virol. 2012 Dec;86(23):12494-502. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01705-12. Epub 2012 Sep 26. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 23015699 Free PMC article.
-
CpG-methylation regulates a class of Epstein-Barr virus promoters.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Sep 23;6(9):e1001114. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001114. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20886097 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) EB1/Zta protein provided in trans and competent for the activation of productive cycle genes does not activate the BZLF1 gene in the EBV genome.J Gen Virol. 1996 Mar;77 ( Pt 3):501-9. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-77-3-501. J Gen Virol. 1996. PMID: 8601788
-
Regulation of cellular and viral protein expression by the Epstein-Barr virus transcriptional regulator Zta: implications for therapy of EBV associated tumors.Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Jun;8(11):987-95. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.11.8369. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19448399 Review.
-
Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses.Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:81-109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419942 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancer Control of MicroRNA miR-155 Expression in Epstein-Barr Virus-Infected B Cells.J Virol. 2018 Sep 12;92(19):e00716-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00716-18. Print 2018 Oct 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30021904 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Role of Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 in Immune Modulation: A Multifaced Signalling Perspective.Viruses. 2024 Apr 4;16(4):564. doi: 10.3390/v16040564. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Implications of Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Genes in Carcinogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 24;14(23):5780. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235780. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying the key regulators orchestrating Epstein-Barr virus reactivation.Front Microbiol. 2024 Dec 5;15:1505191. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1505191. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39703703 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Longnecker R, Kieff E, Cohen JI. Epstein-Barr virus/Replication and Epstein-Barr virus. In: Knipe D, Howley P, editors. Fields Virology. 6 ed. Baltimore, USA: Lippencott, Williams, Wilkins; 2013. (editors)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

