Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Coronary Artery Disease (from the Million Veteran Program)
- PMID: 29580627
- PMCID: PMC6734183
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.01.042
Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Coronary Artery Disease (from the Million Veteran Program)
Abstract
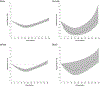
Moderate alcohol consumption has been associated with a lower risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) in the general population but has not been well studied in US veterans. We obtained self-reported alcohol consumption from Million Veteran Program participants. Using electronic health records, CAD events were defined as 1 inpatient or 2 outpatient diagnosis codes for CAD, or 1 code for a coronary procedure. We excluded participants with prevalent CAD (n = 69,995) or incomplete alcohol information (n = 8,449). We used a Cox proportional hazards model to estimate hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals for CAD, adjusting for age, gender, body mass index, race, smoking, education, and exercise. Among 156,728 participants, the mean age was 65.3 years (standard deviation = 12.1) and 91% were men. There were 6,153 CAD events during a mean follow-up of 2.9 years. Adjusted hazard ratios (95% confidence intervals) for CAD were 1.00 (reference), 1.02 (0.92 to 1.13), 0.83 (0.74 to 0.93), 0.77 (0.67 to 0.87), 0.71 (0.62 to 0.81), 0.62 (0.51 to 0.76), 0.58 (0.46 to 0.74), and 0.95 (0.85 to 1.06) for categories of never drinker; former drinker; current drinkers of ≤0.5 drink/day, >0.5 to 1 drink/day, >1 to 2 drinks/day, >2 to 3 drinks/day, and >3 to 4 drinks/day; and heavy drinkers (>4 drinks/day) or alcohol use disorder, respectively. For a fixed amount of ethanol, intake at ≥3 days/week was associated with lower CAD risk compared with ≤1 day/week. Beverage preference (beer, wine, or liquor) did not influence the alcohol-CAD relation. Our data show a lower risk of CAD with light-to-moderate alcohol consumption among US veterans, and drinking frequency may provide a further reduction in risk.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
This publication does not represent the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government. There are no conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavjou OA, Butler J, Dracup K, Ezekowitz MD, Finkelstein EA, Hong Y, Johnston SC, Khera A, Lloyd-Jones DM, Nelson SA, Nichol G, Orenstein D, Wilson PW, Woo YJ, American Heart Association Advocacy Coordinating C, Stroke C, Council on Cardiovascular R, Intervention, Council on Clinical C, Council on E, Prevention, Council on A, Thrombosis, Vascular B, Council on C, Critical C, Perioperative, Resuscitation, Council on Cardiovascular N, Council on the Kidney in Cardiovascular D, Council on Cardiovascular S, Anesthesia, Interdisciplinary Council on Quality of C, Outcomes R. Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011;123:933–944. - PubMed
-
- Costanzo S, Di Castelnuovo A, Donati MB, Iacoviello L, de Gaetano G. Wine, beer or spirit drinking in relation to fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events: a meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol 2011;26:833–850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

