19q13.12 microdeletion syndrome fibroblasts display abnormal storage of cholesterol and sphingolipids in the endo-lysosomal system
- PMID: 29580926
- PMCID: PMC6394866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.03.020
19q13.12 microdeletion syndrome fibroblasts display abnormal storage of cholesterol and sphingolipids in the endo-lysosomal system
Abstract
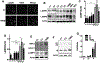
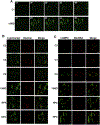
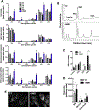
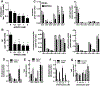
Microdeletions in 19q12q13.12 cause a rare and complex haploinsufficiency syndrome characterized by intellectual deficiency, developmental delays, and neurological movement disorders. Variability in the size and interval of the deletions makes it difficult to attribute the complex clinical phenotype of this syndrome to an underlying gene(s). As an alternate approach, we examined the biochemical and metabolic features of fibroblasts from an affected individual to derive clues as to the molecular basis for the syndrome. Immunofluorescence and electron microscopy of affected fibroblasts revealed an abnormal endo-lysosomal compartment that was characterized by rapid accumulation of lysosomotropic dyes, elevated LAMP1 and LAMP2 expression and vacuoles containing membrane whorls, common features of lysosomal lipid storage disorders. The late endosomes-lysosomes (LE/LY) of affected fibroblasts accumulated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and displayed reduced cholesterol esterification and increased de novo cholesterol synthesis, indicative of defective cholesterol transport to the endoplasmic reticulum. Affected fibroblasts also had increased ceramide and sphingolipid mass, altered glycosphingolipid species and accumulation of a fluorescent lactosylceramide probe in LE/LY. Autophagosomes also accumulated in affected fibroblasts because of decreased fusion with autolysosomes, a defect associated with other lysosomal storage diseases. Attempts to correct the cholesterol/sphingolipid storage defect in fibroblasts with cyclodextrin, sphingolipid synthesis inhibitors or by altering ion transport were unsuccessful. Our data show that 19q13.12 deletion fibroblasts have abnormal accumulation of cholesterol and sphingolipids in the endo-lysosomal system that compromises organelle function and could be an underlying cause of the clinical features of the syndrome.
Keywords: Autophagy; Cholesterol; Chromosome 19 deletion syndrome; Lipid storage disorder; Lysosomes; Sphingolipids.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


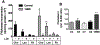
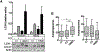
Similar articles
-
Accumulation of sphingolipids in SAP-precursor (prosaposin)-deficient fibroblasts occurs as intralysosomal membrane structures and can be completely reversed by treatment with human SAP-precursor.Eur J Cell Biol. 1997 May;73(1):10-8. Eur J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9174667
-
Sphingolipids and neuronal degeneration in lysosomal storage disorders.J Neurochem. 2019 Mar;148(5):600-611. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14540. Epub 2018 Aug 16. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 29959861 Review.
-
A lysosome-plasma membrane-sphingolipid axis linking lysosomal storage to cell growth arrest.FASEB J. 2018 Oct;32(10):5685-5702. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701512RR. Epub 2018 May 10. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29746165 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Drosophila Saposin-related mutants as a model for lysosomal sphingolipid storage diseases.Dis Model Mech. 2017 Jun 1;10(6):737-750. doi: 10.1242/dmm.027953. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Dis Model Mech. 2017. PMID: 28389479 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids and lysosomal pathologies.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1841(5):799-810. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.015. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24184515 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone lysine methyltransferase-related neurodevelopmental disorders: current knowledge and saRNA future therapies.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 27;11:1090046. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1090046. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36923252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KMT2B-related disorders: expansion of the phenotypic spectrum and long-term efficacy of deep brain stimulation.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 10:arXiv:2502.06320v1. ArXiv. 2025. Update in: Brain. 2020 Dec 5;143(11):3242-3261. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa304. PMID: 39990802 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Construction of copy number variation landscape and characterization of associated genes in a Bangladeshi cohort of neurodevelopmental disorders.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 7;14:955631. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.955631. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36959829 Free PMC article.
-
KMT2B-related disorders: expansion of the phenotypic spectrum and long-term efficacy of deep brain stimulation.Brain. 2020 Dec 5;143(11):3242-3261. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa304. Brain. 2020. PMID: 33150406 Free PMC article.
-
Update on KMT2B-Related Dystonia.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019 Nov 25;19(11):92. doi: 10.1007/s11910-019-1007-y. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31768667 Review.
References
-
- Chowdhury S, Bandholz AM, Parkash S, Dyack S, Rideout AL, Leppig KA, Thiese H, Wheeler PG, Tsang M, Ballif BC, Shaffer LG, Torchia BS, Ellison JW, Rosenfeld JA, Phenotypic and molecular characterization of 19q12q13.1 deletions: a report of five patients, Am. J. Med. Genet. A 164A (2014) 62–69. - PubMed
-
- Malan V, Raoul O, Firth HV, Royer G, Turleau C, Bernheim A, Willatt L, Munnich A, Vekemans M, Lyonnet S, Cormier-Daire V, Colleaux L, 19q13.11 deletion syndrome: a novel clinically recognisable genetic condition identified by array comparative genomic hybridisation, J. Med. Genet 46 (2009) 635–640. - PubMed
-
- Gana S, Veggiotti P, Sciacca G, Fedeli C, Bersano A, Micieli G, Maghnie M, Ciccone R, Rossi E, Plunkett K, Bi W, Sutton VR, Zuffardi O, 19q13.11 cryptic deletion: description of two new cases and indication for a role of WTIP haploinsufficiency in hypospadias, Eur. J. Hum. Genet 20 (2012) 852–856. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meyer E, Carss KJ, Rankin J, Nichols JM, Grozeva D, Joseph AP, Mencacci NE, Papandreou A, Ng J, Barral S, Ngoh A, Ben-Pazi H, Willemsen MA, Arkadir D, Barnicoat A, Bergman H, Bhate S, Boys A, Darin N, Foulds N, Gutowski N, Hills A, Houlden H, Hurst JA, Israel Z, Kaminska M, Limousin P, Lumsden D, McKee S, Misra S, Mohammed SS, Nakou V, Nicolai J, Nilsson M, Pall H, Peall KJ, Peters GB, Prabhakar P, Reuter MS, Rump P, Segel R, Sinnema M, Smith M, Turnpenny P, White SM, Wieczorek D, Wiethoff S, Wilson BT, Winter G, Wragg C, Pope S, Heales SJ, Morrogh D, Consortium UK, Deciphering Developmental Disorders S, Consortium NBRD, Pittman A, Carr LJ, Perez-Duenas B, Lin JP, Reis A, Gahl WA, Toro C, Bhatia KP, Wood NW, Kamsteeg EJ, Chong WK, Gissen P, Topf M, Dale RC, Chubb JR, Raymond FL, Kurian MA, Mutations in the histone methyltransferase gene KMT2B cause complex early-onset dystonia, Nat. Genet 49 (2017) 223–237. - PubMed
-
- Schuurs-Hoeijmakers JH, Vermeer S, van Bon BW, Pfundt R, Marcelis C, de Brouwer AP, de Leeuw N, de Vries BB, Refining the critical region of the novel 19q13.11 microdeletion syndrome to 750 Kb, J. Med. Genet 46 (2009) 421–423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

