PUMA amplifies necroptosis signaling by activating cytosolic DNA sensors
- PMID: 29581256
- PMCID: PMC5899441
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1717190115
PUMA amplifies necroptosis signaling by activating cytosolic DNA sensors
Abstract
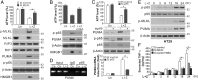
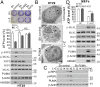
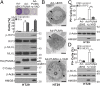
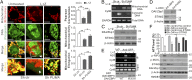
Necroptosis, a form of regulated necrotic cell death, is governed by RIP1/RIP3-mediated activation of MLKL. However, the signaling process leading to necroptotic death remains to be elucidated. In this study, we found that PUMA, a proapoptotic BH3-only Bcl-2 family member, is transcriptionally activated in an RIP3/MLKL-dependent manner following induction of necroptosis. The induction of PUMA, which is mediated by autocrine TNF-α and enhanced NF-κB activity, contributes to necroptotic death in RIP3-expressing cells with caspases inhibited. On induction, PUMA promotes the cytosolic release of mitochondrial DNA and activation of the DNA sensors DAI/Zbp1 and STING, leading to enhanced RIP3 and MLKL phosphorylation in a positive feedback loop. Furthermore, deletion of PUMA partially rescues necroptosis-mediated developmental defects in FADD-deficient embryos. Collectively, our results reveal a signal amplification mechanism mediated by PUMA and cytosolic DNA sensors that is involved in TNF-driven necroptotic death in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: MLKL; NF-κB; PUMA; RIP3; necroptosis.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ofengeim D, Yuan J. Regulation of RIP1 kinase signalling at the crossroads of inflammation and cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:727–736. - PubMed
-
- Pasparakis M, Vandenabeele P. Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature. 2015;517:311–320. - PubMed
-
- Sun L, Wang X. A new kind of cell suicide: Mechanisms and functions of programmed necrosis. Trends Biochem Sci. 2014;39:587–593. - PubMed
-
- He S, et al. Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell. 2009;137:1100–1111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

