Advanced body composition assessment: from body mass index to body composition profiling
- PMID: 29581385
- PMCID: PMC5992366
- DOI: 10.1136/jim-2018-000722
Advanced body composition assessment: from body mass index to body composition profiling
Abstract
This paper gives a brief overview of common non-invasive techniques for body composition analysis and a more in-depth review of a body composition assessment method based on fat-referenced quantitative MRI. Earlier published studies of this method are summarized, and a previously unpublished validation study, based on 4753 subjects from the UK Biobank imaging cohort, comparing the quantitative MRI method with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is presented. For whole-body measurements of adipose tissue (AT) or fat and lean tissue (LT), DXA and quantitative MRIs show excellent agreement with linear correlation of 0.99 and 0.97, and coefficient of variation (CV) of 4.5 and 4.6 per cent for fat (computed from AT) and LT, respectively, but the agreement was found significantly lower for visceral adipose tissue, with a CV of >20 per cent. The additional ability of MRI to also measure muscle volumes, muscle AT infiltration and ectopic fat, in combination with rapid scanning protocols and efficient image analysis tools, makes quantitative MRI a powerful tool for advanced body composition assessment.
Keywords: body composition; magnetic resonance imaging.
© American Federation for Medical Research (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MB, JW, TR and ODL are employees and stockholders of AMRA Medical AB.
Figures

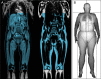

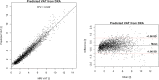
References
-
- Snyder WS. Report of the Task group on reference man: a report Oxford: Pergamon; 1975;1975.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 17702/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585827/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 21231/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 21231/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585819/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 17702/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A620_1014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400491/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585824/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HTA/10/33/04/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

