Factors affecting walking ability in female patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 29584787
- PMCID: PMC5870996
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195059
Factors affecting walking ability in female patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To determine the factors associated with gait parameters in female patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: The gait analysis was performed in a large cohort of RA patients, and three basic gait parameters (step length, cadence and gait speed) were calculated. Clinical and laboratory data were also collected. Factors associated with gait parameters were analyzed using multivariable linear regression in the three models with forced entry. Then, we divided those patients with Health Assessment Questionnaire disability index (HAQ) scores ≤ 0.5 into two groups according to their gait speed that were compared to identify the characteristics of patients with a good HAQ score but poor walking ability.
Results: A total of 318 female patients were analyzed. Knee extension strength had the strongest positive association with all three gait parameters (P < 0.0001), while methotrexate use was also positively associated with all three gait parameters (step length: P < 0.05, cadence: P < 0.05 in model 1 and 2; P < 0.01 in model 3, gait speed: P < 0.01). The disease activity score was negatively associated with step length and gait speed (step length, gait speed: P < 0.01 in model 1 and 2; P < 0.05 in model 3). 26% of patients with good HAQ scores showed slow gait speed. Patients with good HAQ scores and slow gait speed had higher disease activity scores (P < 0.05) and lower knee extension strength (P < 0.0001) than those with good HAQ scores and normal gait speed.
Conclusions: High knee extension strength, low disease activity and administration of methotrexate were strongly associated with good walking ability in female patients with RA. And, even if patients showed good HAQ scores, about quarter of those patients had poor walking ability, and they showed higher disease activity, lower knee extension strength, compared to the patients with normal gait speed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
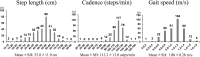



Similar articles
-
Quantifying gait deviations in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis using the Gait Deviation Index.Scand J Rheumatol. 2014;43(2):124-31. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2013.822095. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Scand J Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24090053
-
Muscle strength, pain, and disease activity explain individual subdimensions of the Health Assessment Questionnaire disability index, especially in women with rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Jan;65(1):30-4. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.034769. Epub 2005 May 18. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 15901635 Free PMC article.
-
Change in Gait Deviation Index after anti-tumour necrosis factor-α treatment in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot study.Scand J Rheumatol. 2013;42(5):356-61. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2013.776102. Epub 2013 Apr 14. Scand J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23581251 Clinical Trial.
-
Gait pattern in rheumatoid arthritis.Gait Posture. 2008 Aug;28(2):229-34. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2007.12.001. Epub 2008 Jan 15. Gait Posture. 2008. PMID: 18226528
-
Examination of factors affecting gait properties in healthy older adults: focusing on knee extension strength, visual acuity, and knee joint pain.J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2014 Apr-Jun;37(2):52-7. doi: 10.1519/JPT.0b013e318295daba. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2014. PMID: 23835771
Cited by
-
The effects of resistance training with blood flow restriction on muscle strength, muscle hypertrophy and functionality in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review with meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 10;16(11):e0259574. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259574. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34758045 Free PMC article.
-
Association of knee osteoarthritis grade with one-leg standing balance and quadriceps strength in male independent ambulators aged ≥80 years.J Orthop. 2020 Mar 24;21:79-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2020.03.013. eCollection 2020 Sep-Oct. J Orthop. 2020. PMID: 32255985 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive relationship between disease activity indices, mTSS, and mHAQ and physical function evaluation and QOL in females with rheumatoid arthritis.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 11;13(1):21905. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49380-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38081947 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Low-Speed and High-Speed Resistance Training Programs on Frailty Status, Physical Performance, Cognitive Function, and Blood Pressure in Prefrail and Frail Older Adults.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 26;8:702436. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.702436. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34381802 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between physical activity and functional limitations in Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander middle-aged and older adults in the United States.Ethn Health. 2022 Oct;27(7):1616-1629. doi: 10.1080/13557858.2021.1921120. Epub 2021 May 5. Ethn Health. 2022. PMID: 33951984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carmona L, Villaverde V, Hernandez-Garcia C, Ballina J, Gabriel R, Laffon A. The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the general population of Spain. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002;41(1):88–95. Epub 2002/01/17. . - PubMed
-
- Gabriel SE, Crowson CS, O'Fallon WM. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis in Rochester, Minnesota, 1955–1985. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42(3):415–20. Epub 1999/03/24. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199904)42:3<415::AID-ANR4>3.0.CO;2-Z . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Silman AJ, Pearson JE. Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis research. 2002;4 Suppl 3:S265–72. Epub 2002/07/12. doi: 10.1186/ar578 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3240153. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uhlig T, Heiberg T, Mowinckel P, Kvien TK. Rheumatoid arthritis is milder in the new millennium: health status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis 1994–2004. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(12):1710–5. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.084673 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rubbert-Roth A, Finckh A. Treatment options in patients with rheumatoid arthritis failing initial TNF inhibitor therapy: a critical review. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11 Suppl 1:S1 Epub 2009/04/25. doi: 10.1186/ar2666 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2669237. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

