Functional network integration and attention skills in young children
- PMID: 29587178
- PMCID: PMC6969078
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dcn.2018.03.007
Functional network integration and attention skills in young children
Abstract
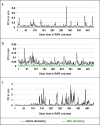
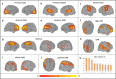
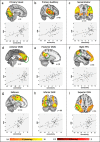
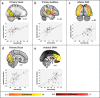
Children acquire attention skills rapidly during early childhood as their brains undergo vast neural development. Attention is well studied in the adult brain, yet due to the challenges associated with scanning young children, investigations in early childhood are sparse. Here, we examined the relationship between age, attention and functional connectivity (FC) during passive viewing in multiple intrinsic connectivity networks (ICNs) in 60 typically developing girls between 4 and 7 years whose sustained, selective and executive attention skills were assessed. Visual, auditory, sensorimotor, default mode (DMN), dorsal attention (DAN), ventral attention (VAN), salience, and frontoparietal ICNs were identified via Independent Component Analysis and subjected to a dual regression. Individual spatial maps were regressed against age and attention skills, controlling for age. All ICNs except the VAN showed regions of increasing FC with age. Attention skills were associated with FC in distinct networks after controlling for age: selective attention positively related to FC in the DAN; sustained attention positively related to FC in visual and auditory ICNs; and executive attention positively related to FC in the DMN and visual ICN. These findings suggest distributed network integration across this age range and highlight how multiple ICNs contribute to attention skills in early childhood.
Keywords: Attention; Children; Early childhood; Functional connectivity; ICA; Neural networks.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aarts E., Roelofs A. Attentional control in anterior cingulate cortex based on probabilistic cueing. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2011;23:716–727. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson J., Braddick O. From genes to brain development to phenotypic behavior: dorsal-stream vulnerability in relation to spatial cognition, attention, and planning of actions in Williams syndrome (WS) and other developmental disorders. Prog. Brain Res. 2011;189:261–283. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann C.F., Smith S.M. Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2004;23:137–152. - PubMed
-
- Betzel R.F., Byrge L., He Y., Goñi J., Zuo X.N., Sporns O. Changes in structural and functional connectivity among resting-state networks across the human lifespan. Neuroimage. 2014;102(Pt. 2):345–357. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

