Plant-Derived Anticancer Agents: Lessons from the Pharmacology of Geniposide and Its Aglycone, Genipin
- PMID: 29587429
- PMCID: PMC6027249
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines6020039
Plant-Derived Anticancer Agents: Lessons from the Pharmacology of Geniposide and Its Aglycone, Genipin
Abstract
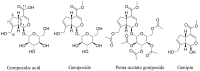
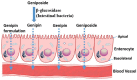
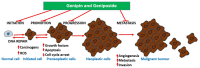
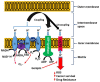
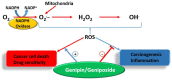
For centuries, plants have been exploited by mankind as sources of numerous cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Good examples of anticancer compounds of clinical significance today include the taxanes (e.g., taxol), vincristine, vinblastine, and the podophyllotoxin analogues that all trace their origin to higher plants. While all these drugs, along with the various other available therapeutic options, brought some relief in cancer management, a real breakthrough or cure has not yet been achieved. This critical review is a reflection on the lessons learnt from decades of research on the iridoid glycoside geniposide and its aglycone, genipin, which are currently used as gold standard reference compounds in cancer studies. Their effects on tumour development (carcinogenesis), cancer cell survival, and death, with particular emphasis on their mechanisms of actions, are discussed. Particular attention is also given to mechanisms related to the dual pro-oxidant and antioxidant effects of these compounds, the mitochondrial mechanism of cancer cell killing through reactive oxygen species (ROS), including that generated through the uncoupling protein-2 (UCP-2), the inflammatory mechanism, and cell cycle regulation. The implications of various studies for the evaluation of glycosidic and aglycone forms of natural products in vitro and in vivo through pharmacokinetic scrutiny are also addressed.
Keywords: apoptosis; cancer; carcinogenesis; genipin; geniposide; metastasis; reactive oxygen species; uncoupling protein 2.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ke X., Shen L. Molecular targeted therapy of cancer: The progress and future prospect. Front. Lab. Med. 2017;1:69–75. doi: 10.1016/j.flm.2017.06.001. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

