The Impact of T-2 Toxin on Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide-Like Immunoreactive (VIP-LI) Nerve Structures in the Wall of the Porcine Stomach and Duodenum
- PMID: 29587461
- PMCID: PMC5923304
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10040138
The Impact of T-2 Toxin on Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide-Like Immunoreactive (VIP-LI) Nerve Structures in the Wall of the Porcine Stomach and Duodenum
Abstract
T-2 toxin is a secondary metabolite of some Fusarium species. It is well-known that this substance can harmfully impact living organisms. Among others, thanks to the ability of crossing the blood-brain barrier, T-2 toxin can affect the central nervous system. Mycotoxins mostly get into the organism through the digestive tract; therefore, first of all they have to break the intestinal barrier, wherein the important component is the enteric nervous system (ENS). However, knowledge about the impact of T-2 toxin on the ENS is rather scant. As a result of the influence of various physiological and pathological agents, ENS can undergo adaptive and reparative processes which manifest as changes in the immunoreactivity of perikaryons for neuronal active substances. So, the aim of the present investigation was to study how low doses of T-2 toxin affect vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-like immunoreactive (VIP-LI) nervous structures in the ENS of the porcine stomach and duodenum. Obtained results have shown that T-2 toxin causes an percentage increase of VIP-LI nerve cells and nerve fibers in every enteric plexus in both fragments of gastrointestinal tract studied. This shows that even low doses of T-2 toxin can have an influence on living organisms.
Keywords: T-2 toxin; enteric nervous system; pig; vasoactive intestinal polypeptide.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
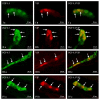


References
-
- Lewis L., Onsongo M., Njapau H., Schurz-Rogers H., Luber G., Kieszak S., Nyamongo J., Backer L., Dahiye A.M., Misore A., et al. Kenya Aflatoxicosis Investigation Group. Aflatoxin contamination of commercial maize products during an outbreak of acute aflatoxicosis in eastern and central Kenya. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005;113:1763–1767. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7998. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moretti A., Logrieco A.F., Susca A. Mycotoxins: An underhand food problem. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017;1542:3–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

