Expression of Reg IV and SOX9 and their correlation in human gastric cancer
- PMID: 29587675
- PMCID: PMC5870489
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4285-x
Expression of Reg IV and SOX9 and their correlation in human gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Reg IV is a member of the regenerating gene family and has been demonstrated to be overexpressed in gastric cancer. However, the functional mechanism of Reg IV in gastric cancer is still unclear.
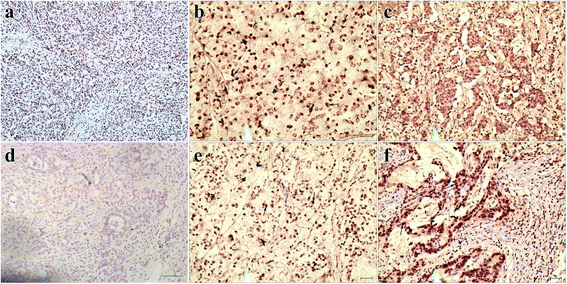
Methods: Expression of Reg IV and SOX9 were investigated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and real-time PCR, and the correlation between the expression of Reg IV and SOX9 was analyzed in gastric cancer tissues. Reg IV expression vectors and a siRNA of Reg IV and SOX9 were transfected into human gastric cancer cells and the protein and mRNA levels of Reg IV and SOX9 were investigated by western blot and real-time PCR. The invasion and migration ability of gastric cancer cells with overexpressed Reg IV and with gene silence of Reg IV and SOX9 were examined by transwell chambers and wound healing assay.
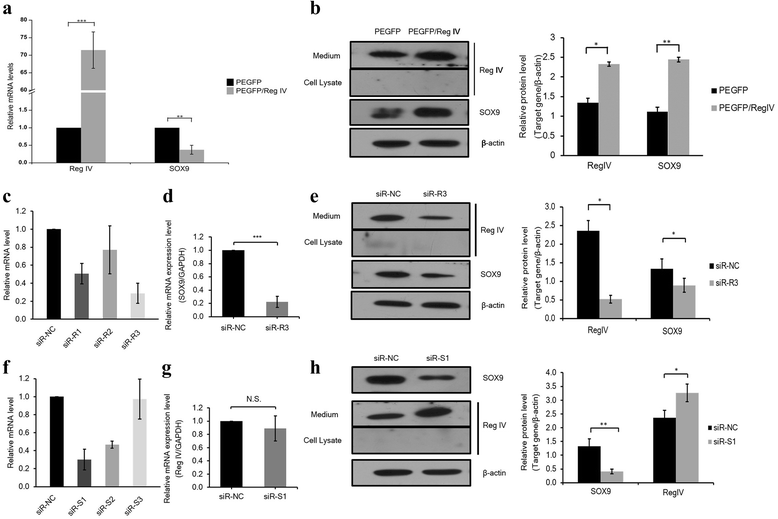
Results: The Reg IV and SOX9 protein expression levels were both significantly higher in gastric cancer tissues compared with adjacent tissues (p = 0.022, p = 0.003). Reg IV protein expression significantly correlated with tumor invasion depth (p < 0.001), but had no significant correlations with age, clinical stage or lymph node metastasis. SOX9 protein expression also had no significant correlations with age, clinical stage, tumor invasion depth or lymph node metastasis. Reg IV transcript expression demonstrated a significant correlation with invasion depth and lymph node metastasis (p = 0.005, p < 0.001) and no significant correlations with age, clinical stage, tumor tissue differentiation or tumor size. SOX9 transcript expression demonstrated a significant correlation with invasion depth and tumor tissue differentiation (p = 0.044, p = 0.007) and no significant correlations with age, clinical stage or tumor size. The Reg IV expression showed a positive correlation with the SOX9 expression (p < 0.000, p = 0.008). Overexpression of Reg IV could upregulate SOX9 expression and promote invasiveness and migration of tumor cells, and silencing of Reg IV could downregulate SOX9 and inhibit invasiveness and migration of tumor cells in MKN-45 and AGS cells. On the other hand, silencing of SOX9 could upregulate Reg IV protein expression.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated that Reg IV positively regulates the expression of SOX9 and is involved in tumor cell invasion and migration in gastric cancer.
Keywords: Correlation; Gastric cancer; Reg IV; SOX9.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The protocols involving tumor tissues from patients with gastric cancer in this study were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Medicine and Science Research Institute of Gansu Province (reference number: P201108150024). All study participants provided informed consent to participate in the study.
Consent for publication
Each patient agreed with using their individual data under anonymity.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CDX2 and Reg IV expression and correlation in gastric cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Feb 27;21(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01678-9. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33639844 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of human kallikrein 12 gene expression in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Dec 7;18(45):6597-604. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i45.6597. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23236234 Free PMC article.
-
HOX transcript antisense intergenic RNA represses E-cadherin expression by binding to EZH2 in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Sep 7;23(33):6100-6110. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6100. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28970725 Free PMC article.
-
Reg gene family and human diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Dec;9(12):2635-41. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2635. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 14669303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic relevance of SOX9 stem cell factor in gastric cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019 Feb;23(2):143-152. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2019.1559826. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019. PMID: 30572738 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential carcinogenic role of Reg IV in ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal neoplasia.Ecancermedicalscience. 2024 Aug 29;18:1751. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2024.1751. eCollection 2024. Ecancermedicalscience. 2024. PMID: 39421174 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of REG IV gene in human intestinal epithelial cells by lipopolysaccharide via downregulation of microRNA-24.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Sep;26(17):4710-4720. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17498. Epub 2022 Aug 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35946046 Free PMC article.
-
REG4 promotes the proliferation and anti-apoptosis of cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 12;10:1012193. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1012193. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36172286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and Clinical Relevance of SOX9 in Gastric Cancer.Dis Markers. 2019 Jun 2;2019:8267021. doi: 10.1155/2019/8267021. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 31275454 Free PMC article.
-
CDX2 and Reg IV expression and correlation in gastric cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Feb 27;21(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01678-9. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33639844 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

