Exploring the potential of black tea based flavonoids against hyperlipidemia related disorders
- PMID: 29592809
- PMCID: PMC5872535
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-018-0688-6
Exploring the potential of black tea based flavonoids against hyperlipidemia related disorders
Abstract
Background: In recent decade, Hyperlipidemia related disorders like obesity, hypercholesterolemia and diabetes are considered as the leading killers for mankind. Fundamental nexus between nutrition and health diverting the consumers focus towards plant based natural products as a remedy against various metabolic syndrome. Considering this, present study was conducted to explicate the role of black tea polyphenols such as Theaflavins and thearubigins therapeutic potential to tackle targeted maladies especially oxidative stress related disorders like hypercholesterolemia and diabetes.
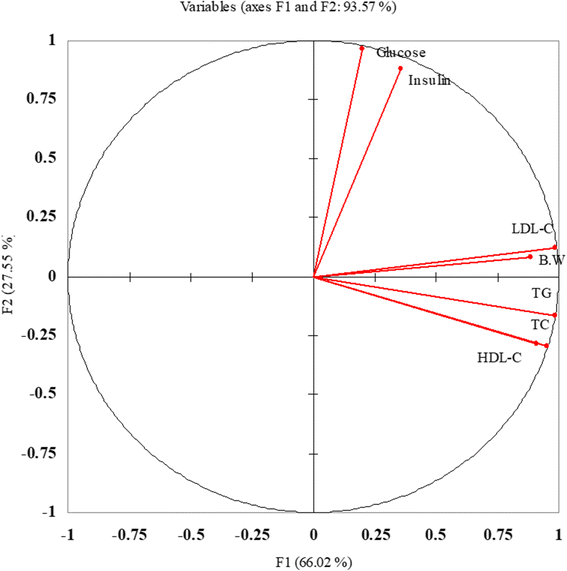
Methods: The mandate of current investigation was to explore the hypoglycemic and hypocholestrolemic perspective of isolated theaflavin and thearubigins through a model feeding trial. For the purpose, theaflavin & thearubigins were isolated from black tea through solvent partition method and utilize to form three types of nutraceutical drinks (theaflavin, thearubigins & theaflavin + thearubigins based) alongside control to be further utilized in bioefficacy trial. In bioefficacy trial, three types of independent studies were design on the bases of diet by involving 20 male wistar rats in each study (5 for each group). In study I, normal diet was administrated while, in study II & III high cholesterol and high sucrose diet was given, respectively along with prepared nutraceutical drinks to synchronize their therapeutic effect for a period of 56 days. At the termination of trial, Feed & drink intakes, body weight, total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglycerides, glucose and insulin levels were measured.
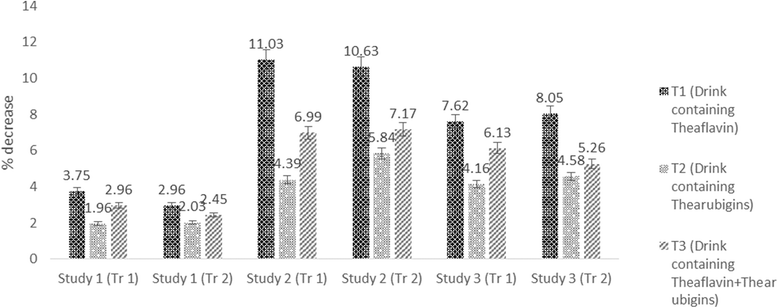
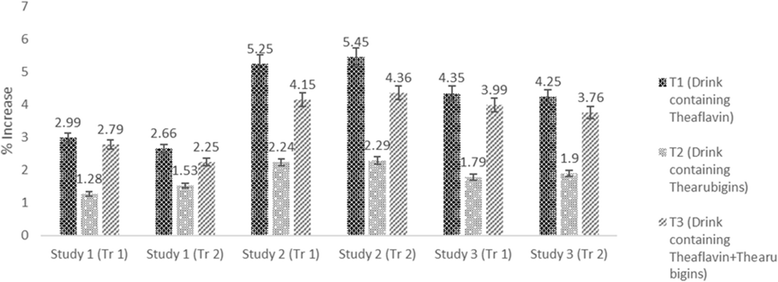
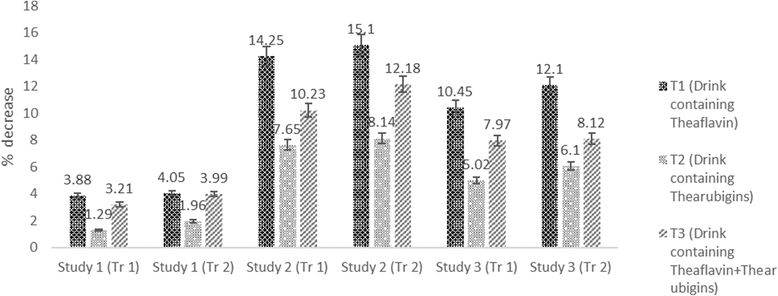
Results: The results indicated reduction in cholesterol, LDL and triglycerides levels of experimental rats in all studies with significant increase in HDL. In this context, theaflavin based drink imparted maximum reduction in cholesterol (3.75, 11.03 & 10.39%), LDL (3.84, 14.25& 10.84%) & triglycerides (2.99, 8.54 & 6.65%) in respective studies compared to thearubigins and theaflavin + thearubigins based drinks. However, theaflavin+ thearubigins based drink caused highest glucose decline and maximum insulin increase in all studies as compared to other nutraceutical drinks. The reported value for the insulin increase were 13.02 ± 1.02 & 14.55 ± 1.13, 10.09 ± 0.15 & 11.59 ± 0.86 for Hyperglycemic and Hypocholestrolemic rats respectively compared to control (7.84 ± 0.45 & 9.10 ± 0.41) for study I and II.
Conclusions: In the nutshell, theaflavin and thearubigins based dietary interventions are helpful to alleviate the hypercholestrolemia and hyperglycemia and should be promoted as parallel therapy to combat these disorders.
Keywords: Dietary interventions; Flavonoids; Hyperlipidemia; Thearubigins.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures








References
-
- World Health Organization . Prevalence of diabetes in the WHO eastern Mediterranean region. 2006.
-
- Schlesier K, Kühn B, Kiehntop M, Winnefeld K, Roskos M, Bitsch R, Böhm V. Comparative evaluation of green and black tea consumption on the iron status of omnivorous and vegetarian people. Food Res Int. 2012;46:522–527. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.06.019. - DOI
-
- Imran A, Butt MS, Sharif MK. Phytochemical density of some promising commercial tea brands. Int J Food Prop. 2012;15(1):99–108. doi: 10.1080/10942911003754650. - DOI
-
- Alipoor B, Rad AH. A review on the therapeutical effects of tea. Asian J Clin Nutri. 2012;4(1):1–15. doi: 10.3923/ajcn.2012.1.15. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

