Novel microtubule inhibitor MPT0B098 inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 29592811
- PMCID: PMC5875002
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-018-0432-6
Novel microtubule inhibitor MPT0B098 inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
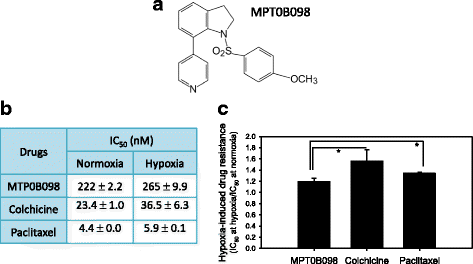
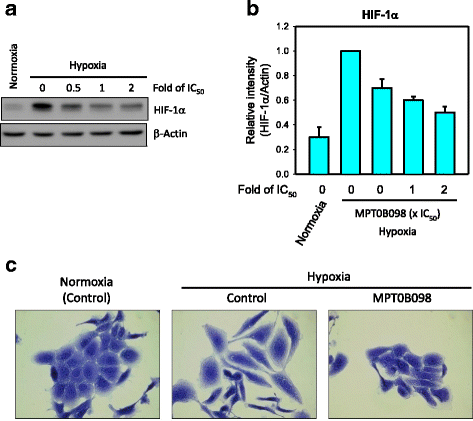
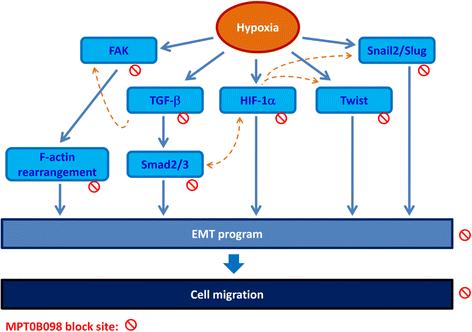
Background: Tumor hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is critical in promoting cancer metastasis. We recently discovered a novel microtubule inhibitor, MPT0B098, that employs a novel antitumor mechanism. It destabilizes hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α mRNA by blocking the function of human antigen R. Thus, we proposed that MPT0B098 modulates hypoxia-induced EMT.
Methods: In vitro IC50 values were determined through the methylene blue dye assay. To investigate molecular events, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, Western blotting, immunofluorescence staining, and wound healing assay were employed.
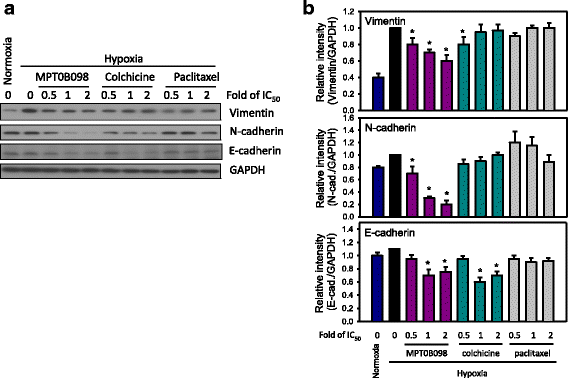
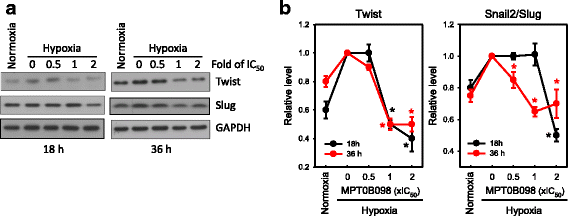
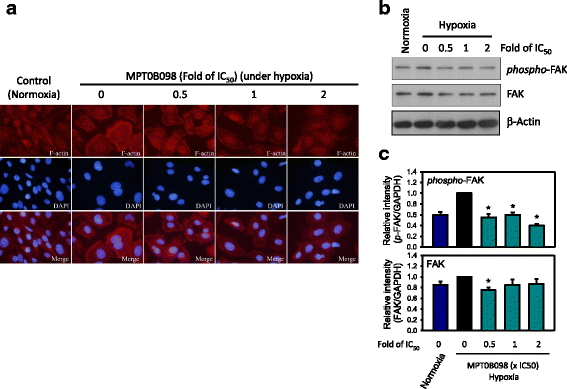
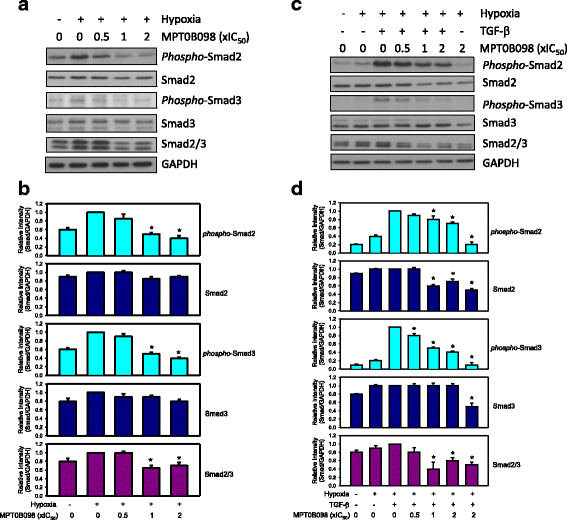
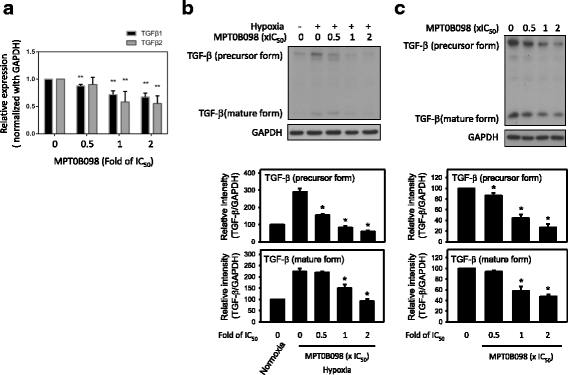
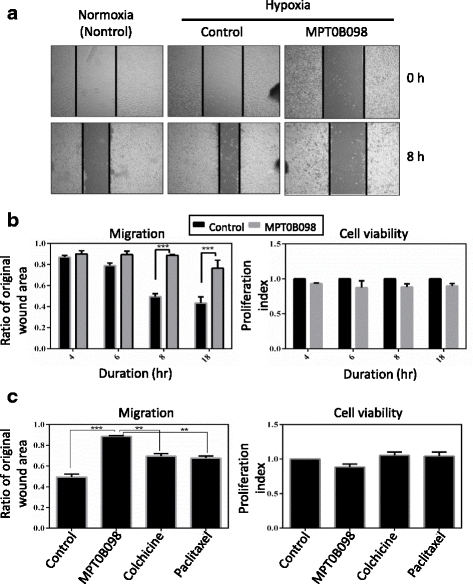
Results: MPT0B098 significantly inhibited HIF-1α expression, epithelial-to-mesenchymal morphology changes, and migratory ability in the human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line OEC-M1. Furthermore, after MPT0B098 treatment, the expression of two mesenchymal markers, vimentin and N-cadherin, was downregulated under hypoxic conditions. Moreover, MPT0B098 suppressed hypoxia-induced EMT in part by inhibiting EMT-activating transcription factors, Twist and SNAI2/Slug. In addition, the inhibition of hypoxia-induced F-actin rearrangement and focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation may have contributed to suppression of EMT by MPT0B098in OEC-M1 cells. MPT0B098 significantly inhibited transforming growth factor(TGF)-β-induced phosphorylation of receptor-associated Smad2/3 by downregulating TGF-β mRNA and protein expression.
Conclusions: Taken together, this study provides a novel insight into the role of MPT0B098 in inhibiting hypoxia-induced EMT, suggesting its potential use for treating head and neck cancers.
Keywords: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition; Head and neck cancer; Hypoxia; Microtubule inhibitor; TGF-β.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No applicable
Consent for publication
No applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Brown JM, Giaccia AJ. The unique physiology of solid tumors: opportunities (and problems) for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 1998;58(7):1408–1416. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

