The Ebb and Flow of Echocardiographic Cardiac Function Parameters in Relationship to Hemodialysis Treatment in Patients with ESRD
- PMID: 29592914
- PMCID: PMC5967760
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2017101102
The Ebb and Flow of Echocardiographic Cardiac Function Parameters in Relationship to Hemodialysis Treatment in Patients with ESRD
Abstract
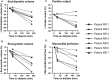
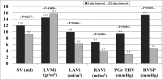
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of mortality in patients receiving hemodialysis. Cardiovascular events in these patients demonstrate a day-of-week pattern; i.e., they occur more commonly during the last day of the long interdialytic interval and the first session of the week. The hemodialysis process causes acute decreases in cardiac chamber size and pulmonary circulation loading and acute diastolic dysfunction, possibly through myocardial stunning and other non-myocardial-related mechanisms; systolic function, in contrast, is largely unchanged. During interdialytic intervals volume overload, acid-base, and electrolyte shifts, as well as arterial and myocardial wall changes, result in dilatation of right cardiac chambers and pulmonary circulation overload. Recent studies suggest that these alterations are more extended during the long interdialytic interval or the first dialysis session of the week and are associated with excess volume overload or removal, respectively, thus adding a mechanism for the day-of-week pattern of mortality in patients receiving hemodialysis. This review summarizes the existing data from echocardiographic studies of cardiac morphology and function during the hemodialysis session, as well as during the interdialytic intervals.
Keywords: diastolic dysfunction; echocardiography; hemodialysis; interdialytic interval; myocardial stunning; pulmonary circulation overload.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- de Jager DJ, Grootendorst DC, Jager KJ, van Dijk PC, Tomas LM, Ansell D, et al. : Cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality among patients starting dialysis. JAMA 302: 1782–1789, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Georgianos PI, Sarafidis PA: Pro: Should we move to more frequent haemodialysis schedules? Nephrol Dial Transplant 30: 18–22, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Zoccali C: Cardiovascular risk in uraemic patients-is it fully explained by classical risk factors? Nephrol Dial Transplant 15: 454–457, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Zoccali C, Bolignano D, Mallamaci F: Left ventricular hypertrophy in chronic kidney disease. In: Oxford Textbook of Clinical Nephrology, 4th Ed., edited by Turner NN, Lameire N, Goldsmith DJ, Winearls CG, Himmelfarb J, Remuzzi G, et al, Oxford, Oxford University Press, 2015, pp 837–852
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

