Drug-induced movement disorder and confusion associated with duloxetine
- PMID: 29592972
- PMCID: PMC5878391
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-216746
Drug-induced movement disorder and confusion associated with duloxetine
Abstract
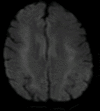
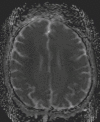
A 60-year-old woman with major depressive disorder, developed high blood pressure, confusion and dyskinesias of face, neck and jaw, following an increase in her dose of duloxetine. Routine blood tests including toxic, infective and metabolic workup were unremarkable. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis and electroencephalogram were also normal. MRI brain showed bilaterally symmetrical diffusion-restricted areas in deep cerebral white matter. Duloxetine was held on suspicion of drug adverse effect. She had complete resolution of symptoms within 48 hours and resolution of MRI brain changes over 6 weeks. Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors such as duloxetine may have the potential to cause drug-induced movement disorders, confusion and high blood pressure and should be used cautiously especially in elderly.
Keywords: hypertension; neurology (drugs and medicines); unwanted effects / adverse reactions.
© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A case of retrobulbar optic neuritis caused by duloxetine.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2016 Sep;35(3):251-3. doi: 10.3109/15569527.2015.1076435. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26362493
-
Duloxetine-related tardive dystonia and tardive dyskinesia: a case report.Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2010 Nov-Dec;32(6):646.e9-646.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2010.04.009. Epub 2010 Jun 3. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 21112461
-
An Open-Label Pilot Study of Duloxetine in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Comorbid Major Depressive Disorder.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2016 Dec;36(6):710-715. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000599. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27755218
-
Duloxetine: a review of its use in the treatment of major depressive disorder.CNS Drugs. 2007;21(7):581-609. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200721070-00004. CNS Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17579500 Review.
-
Excessive sweating induced by interaction between agomelatine and duloxetine hydrochloride: case report and review of the literature.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2015 Sep;127(17-18):703-6. doi: 10.1007/s00508-014-0688-0. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2015. PMID: 25576334 Review.
Cited by
-
Atraumatic trismus induced by duloxetine: an uncommon presentation of acute dystonia.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Feb 4;14(2):e237065. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-237065. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33542006 Free PMC article.
-
Daytime bruxism, tardive orofacial dyskinesia, and dysphagia as side effects to duloxetine use over nine years in an octogenarian.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024 Jul 22;79:100438. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100438. eCollection 2024. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 39043068 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kajdasz DK, Iyengar S, Desaiah D, et al. . Duloxetine for the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: evidence-based findings from post hoc analysis of three multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group studies. Clin Ther 2007;29(Suppl):2536–46. 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.12.002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
