The plasma level changes of VEGF and soluble VEGF receptor-1 are associated with high-altitude pulmonary edema
- PMID: 29593196
- PMCID: PMC6598690
- DOI: 10.2152/jmi.65.64
The plasma level changes of VEGF and soluble VEGF receptor-1 are associated with high-altitude pulmonary edema
Abstract
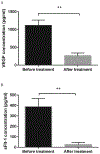
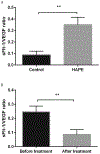
Hypoxia-induced plasma levels of VEGF and sFlt-1 are responsible for increased vascular permeability occurred in both brain and pulmonary edema. Currently, it remains unclear the exact roles of VEGF and sFlt-1 in High Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE) pathogenesis. In this study, plasma levels of VEGF and sFlt-1 from 10 HAPE and 10 non-HAPE subjects were measured and compared. The results showed that plasma levels of both VEGF and sFlt-1 in HAPE patients were significantly increased as compared to the non-HAPE group. Interestingly, increased plasma levels of these two protein factors were markedly reduced after treatments. As compared to VEGF, sFlt-1 was much more affected by hypoxia and treatments, suggesting this factor was a key factor contributed to HAPE pathogenesis. Importantly, the ratio of sFlt-1 and VEGF in group of either non-HAPE or HAPE after recovery was significantly lower than the ratio in HAPE patients prior to treatments. Our findings suggested that sFlt-1 was a key factor that involved in HAPE pathogenesis and the sFlt-1/VEGF ratio could be used as a sensitive diagnostic marker for HAPE. J. Med. Invest. 65:64-68, February, 2018.
Keywords: High altitude pulmonary edema; Soluble VEGF receptor; Vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Changes of VEGF, TNF-alpha, IL-6 and NO in serum of patients with HAPE].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011 May;27(2):201-3. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21845872 Chinese.
-
Effects of hypobaric hypoxia on vascular endothelial growth factor and the acute phase response in subjects who are susceptible to high-altitude pulmonary oedema.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2000 Apr;81(6):497-503. doi: 10.1007/s004210050074. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10774874
-
Greater free plasma VEGF and lower soluble VEGF receptor-1 in acute mountain sickness.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005 May;98(5):1626-9. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00589.2004. Epub 2005 Jan 13. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005. PMID: 15649874
-
[High-altitude pulmonary edema in Japan].Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1995 Dec;33 Suppl:1-6. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1995. PMID: 8752474 Review. Japanese.
-
Heterogeneous pulmonary blood flow in response to hypoxia: a risk factor for high altitude pulmonary edema?Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2006 Apr 28;151(2-3):217-28. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2005.10.007. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16377263 Review.
Cited by
-
EPAS1 and VEGFA gene variants are related to the symptoms of acute mountain sickness in Chinese Han population: a cross-sectional study.Mil Med Res. 2020 Jul 27;7(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40779-020-00264-6. Mil Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32718338 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Microparticles Are Differentially Increased in Lowlanders and Highlanders with High Altitude Induced Pulmonary Hypertension during the Cold Season.Cells. 2022 Sep 20;11(19):2932. doi: 10.3390/cells11192932. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36230894 Free PMC article.
-
The blunted vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) response to high-altitude hypoxia and genetic variants in the promoter region of the VEGFA gene in Sherpa highlanders.PeerJ. 2022 Aug 17;10:e13893. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13893. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35996666 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-121 Administration Mitigates Halogen Inhalation-Induced Pulmonary Injury and Fetal Growth Restriction in Pregnant Mice.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Feb 4;9(3):e013238. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013238. Epub 2020 Feb 3. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32009528 Free PMC article.
-
Low Temperature Plasma Suppresses Lung Cancer Cells Growth via VEGF/VEGFR2/RAS/ERK Axis.Molecules. 2022 Sep 13;27(18):5934. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185934. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Norboo T, Saiyed HN, Angchuk PT, Tsering P, Angchuk ST, Phuntsog ST, Yahya M, Wood S, Bruce NGBall KP: Mini review of high altitude health problems in Ladakh. Journal/Biomed Pharmacother 58: 220–225, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Hackett PRennie D: High-altitude pulmonary edema. Journal/JAMA 287: 2275–2278, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Litch JABishop RA: Reascent following resolution of high altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE). Journal/High Alt Med Biol 2: 53–55, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Dehnert C, Berger MM, Mairbaurl HBartsch P: High altitude pulmonary edema: a pressure-induced leak. Journal/Respir Physiol Neurobiol 158: 266–273, 2007, - PubMed
-
- Maloney J, Wang D, Duncan T, Voelkel NRuoss S: Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor in acute mountain sickness. Journal/Chest 118: 47–52, 2000 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

