The plasma level changes of VEGF and soluble VEGF receptor-1 are associated with high-altitude pulmonary edema
- PMID: 29593196
- PMCID: PMC6598690
- DOI: 10.2152/jmi.65.64
The plasma level changes of VEGF and soluble VEGF receptor-1 are associated with high-altitude pulmonary edema
Abstract
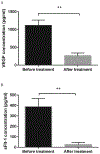
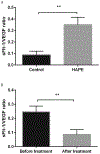
Hypoxia-induced plasma levels of VEGF and sFlt-1 are responsible for increased vascular permeability occurred in both brain and pulmonary edema. Currently, it remains unclear the exact roles of VEGF and sFlt-1 in High Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE) pathogenesis. In this study, plasma levels of VEGF and sFlt-1 from 10 HAPE and 10 non-HAPE subjects were measured and compared. The results showed that plasma levels of both VEGF and sFlt-1 in HAPE patients were significantly increased as compared to the non-HAPE group. Interestingly, increased plasma levels of these two protein factors were markedly reduced after treatments. As compared to VEGF, sFlt-1 was much more affected by hypoxia and treatments, suggesting this factor was a key factor contributed to HAPE pathogenesis. Importantly, the ratio of sFlt-1 and VEGF in group of either non-HAPE or HAPE after recovery was significantly lower than the ratio in HAPE patients prior to treatments. Our findings suggested that sFlt-1 was a key factor that involved in HAPE pathogenesis and the sFlt-1/VEGF ratio could be used as a sensitive diagnostic marker for HAPE. J. Med. Invest. 65:64-68, February, 2018.
Keywords: High altitude pulmonary edema; Soluble VEGF receptor; Vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Norboo T, Saiyed HN, Angchuk PT, Tsering P, Angchuk ST, Phuntsog ST, Yahya M, Wood S, Bruce NGBall KP: Mini review of high altitude health problems in Ladakh. Journal/Biomed Pharmacother 58: 220–225, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Hackett PRennie D: High-altitude pulmonary edema. Journal/JAMA 287: 2275–2278, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Litch JABishop RA: Reascent following resolution of high altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE). Journal/High Alt Med Biol 2: 53–55, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Dehnert C, Berger MM, Mairbaurl HBartsch P: High altitude pulmonary edema: a pressure-induced leak. Journal/Respir Physiol Neurobiol 158: 266–273, 2007, - PubMed
-
- Maloney J, Wang D, Duncan T, Voelkel NRuoss S: Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor in acute mountain sickness. Journal/Chest 118: 47–52, 2000 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

