Oncofetal gene SALL4 reactivation by hepatitis B virus counteracts miR-200c in PD-L1-induced T cell exhaustion
- PMID: 29593314
- PMCID: PMC5871883
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03584-3
Oncofetal gene SALL4 reactivation by hepatitis B virus counteracts miR-200c in PD-L1-induced T cell exhaustion
Abstract
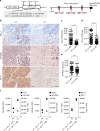
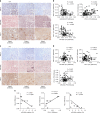
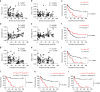
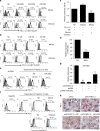
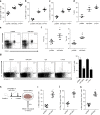
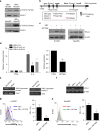
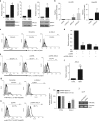
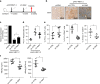
A chronic viral or tumor microenvironment can push T cells to exhaustion by promoting coinhibitory ligand expression. However, how host factors control coinhibitory ligand expression and whether viral infection breaks this control during tumor progress is unknown. Here we show a close negative correlation between SALL4 or PD-L1 and miR-200c in tumors from 98 patients with HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. SALL4 or PD-L1 expression correlates negatively with miR-200c expression, and patients with lower levels of SALL4 or PD-L1 and higher miR-200c survive longer. Moreover, over-expression of miR-200c antagonizes HBV-mediated PD-L1 expression by targeting 3'-UTR of CD274 (encoding PD-L1) directly, and reverses antiviral CD8+ T cell exhaustion. MiR-200c transcription is inhibited by oncofetal protein SALL4, which is re-expressed through HBV-induced STAT3 activation in adulthood. We propose that an HBV-pSTAT3-SALL4-miR-200c axis regulates PD-L1. Therapeutic strategies to influence this axis might reverse virus-induced immune exhaustion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

