Glucagon-like peptide-1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects on mouse colon smooth muscle cells through the cyclic adenosine monophosphate/nuclear factor-κB pathway in vitro
- PMID: 29593427
- PMCID: PMC5865574
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S152835
Glucagon-like peptide-1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects on mouse colon smooth muscle cells through the cyclic adenosine monophosphate/nuclear factor-κB pathway in vitro
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects On Mouse Colon Smooth Muscle Cells Through The Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate/Nuclear Factor-κB Pathway In Vitro [Corrigendum].J Inflamm Res. 2019 Sep 26;12:267. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S230818. eCollection 2019. J Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 31579204 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Intestinal smooth muscle cells (SMCs) undergo substantial morphological, phenotypic, and contractile changes during inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). SMCs act as a source and target for different inflammatory mediators, however their role in IBD pathogenesis is usually overlooked. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an incretin hormone reported to exert multiple anti-inflammatory effects in different tissues including the gastrointestinal tract through various mechanisms.
Aim: The aim of this research is to explore the effect of GLP-1 analog exendin-4 on the expression and secretion of inflammatory markers from mouse colon smooth muscle cells (CSMCs) after stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
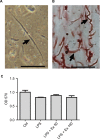
Materials and methods: Freshly isolated CSMCs from male BALB/c mice were cultured in DMEM and treated with vehicle, LPS (1 μg/mL), LPS+exendin-4 (50 nM), or LPS+exendin-4 (100 nM) for 24 h. Expression of inflammatory cytokines was then evaluated by antibody array membrane.
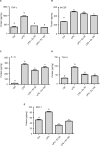
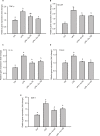
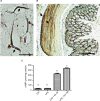
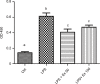
Results: CSMCs showed basal expression of several cytokines which was enhanced with the induction of inflammation by LPS. However, exendin-4 (50 and 100 nM) significantly (p<0.05) reduced the expression of multiple cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1α (IL-1α), T cell activation gene-3 (TCA-3), stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1), and macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSF). To confirm these results, expression of these cytokines was further assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and real-time polymerase chain reaction and similar results were also observed. Moreover, secretion of TNF-α and IL1-α into the conditioned media was significantly downregulated by exendin-4 when compared to LPS-treated cells. Furthermore, LPS increased NF-κB phosphorylation, while exendin-4 significantly reduced levels of NF-κB phosphorylation.
Conclusion: These data indicate that GLP-1 analogs can exert significant anti-inflammatory effects on CSMCs and can potentially be used as an adjunct treatment for inflammatory bowel conditions.
Keywords: GLP-1; inflammation; inflammatory bowel disease; smooth muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Ott C, Schölmerich J. Extraintestinal manifestations and complications in IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10(10):585–595. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

