Downregulation of hsa_circ_0011946 suppresses the migration and invasion of the breast cancer cell line MCF-7 by targeting RFC3
- PMID: 29593432
- PMCID: PMC5865555
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S155923
Downregulation of hsa_circ_0011946 suppresses the migration and invasion of the breast cancer cell line MCF-7 by targeting RFC3
Abstract
Introduction: Although some circRNAs have been found to regulate the progression of malignancies, their functions and coupled molecular mechanisms are still unclear. In our study, we sought to assess the underlying molecular mechanisms of circRNAs in breast cancer and therefore explored the differentially expressed circRNAs and co-expression networks, followed by in vitro experiments.
Materials and methods: High-throughput RNA sequencing was performed to obtain an unbiased profile of circRNA expression. CircRNA-miRNA-mRNA co-expression networks were predicted, and sequence analyses were carried out. The MTT, transwell migration and invasion assay was conducted in Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 cells that had been transfected with si-circRNA and si-negative control (si-NC).
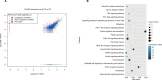
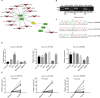
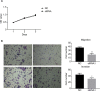
Results: A total of 152 circRNAs were differentially expressed in breast cancer tissues, among which 85 were upregulated and 67 downregulated. Out of these, hsa_circ_0011946 was selected and the subsequent bioinformatics analysis predicted that hsa_circ_0011946 sponging miR-26a/b directly targeted replication factor C subunit 3 (RFC3) and that its knockdown could inhibit RFC3 mRNA and protein expression. Furthermore, hsa_circ_0011946 loss-of-function significantly suppressed the migration and invasion of Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 cells.
Conclusion: Together, these results indicate that hsa_circ_0011946 and RFC3 comprise a novel pathway involved in the progression of breast cancer.
Keywords: MCF-7; RFC; breast cancer; high-throughput sequencing; hsa_circ_0011946.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

