Can Interactions Between α-Synuclein, Dopamine and Calcium Explain Selective Neurodegeneration in Parkinson's Disease?
- PMID: 29593491
- PMCID: PMC5861202
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00161
Can Interactions Between α-Synuclein, Dopamine and Calcium Explain Selective Neurodegeneration in Parkinson's Disease?
Abstract
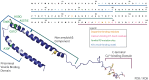
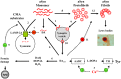
Several lines of evidence place alpha-synuclein (aSyn) at the center of Parkinson's disease (PD) etiology, but it is still unclear why overexpression or mutated forms of this protein affect some neuronal populations more than others. Susceptible neuronal populations in PD, dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and the locus coeruleus (LC), are distinguished by relatively high cytoplasmic concentrations of dopamine and calcium ions. Here we review the evidence for the multi-hit hypothesis of neurodegeneration, including recent papers that demonstrate synergistic interactions between aSyn, calcium ions and dopamine that may lead to imbalanced protein turnover and selective susceptibility of these neurons. We conclude that decreasing the levels of any one of these toxicity mediators can be beneficial for the survival of SNpc and LC neurons, providing multiple opportunities for targeted drug interventions aimed at modifying the course of PD.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; calcium; dopamine; locus coeruleus; multiple hits; substantia nigra pars compacta; α-Synuclein.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

