KV4.3 Expression Modulates NaV1.5 Sodium Current
- PMID: 29593552
- PMCID: PMC5857579
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00178
KV4.3 Expression Modulates NaV1.5 Sodium Current
Abstract
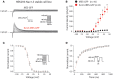
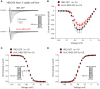
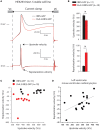
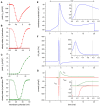
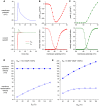
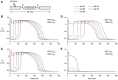
In cardiomyocytes, the voltage-gated transient outward potassium current (Ito) is responsible for the phase-1 repolarization of the action potential (AP). Gain-of-function mutations in KCND3, the gene encoding the Ito carrying KV4.3 channel, have been associated with Brugada syndrome (BrS). While the role of Ito in the pro-arrhythmic mechanism of BrS has been debated, recent studies have suggested that an increased Ito may directly affect cardiac conduction. However, the effects of an increased Ito on AP upstroke velocity or sodium current at the cellular level remain unknown. We here investigated the consequences of KV4.3 overexpression on NaV1.5 current and consequent sodium channel availability. We found that overexpression of KV4.3 protein in HEK293 cells stably expressing NaV1.5 (HEK293-NaV1.5 cells) significantly reduced NaV1.5 current density without affecting its kinetic properties. In addition, KV4.3 overexpression decreased AP upstroke velocity in HEK293-NaV1.5 cells, as measured with the alternating voltage/current clamp technique. These effects of KV4.3 could not be explained by alterations in total NaV1.5 protein expression. Using computer simulations employing a multicellular in silico model, we furthermore demonstrate that the experimentally observed increase in KV4.3 current and concurrent decrease in NaV1.5 current may result in a loss of conduction, underlining the potential functional relevance of our findings. This study gives the first proof of concept that KV4.3 directly impacts on NaV1.5 current. Future studies employing appropriate disease models should explore the potential electrophysiological implications in (patho)physiological conditions, including BrS associated with KCND3 gain-of-function mutations.
Keywords: action potential; arrhythmias; channels; computer simulation; myocyte; sodium current; transient outward current.
Figures

References
-
- Agullo-Pascual E., Lin X., Leo-Macias A., Zhang M., Liang F.-X., Li Z., et al. (2014). Super-resolution imaging reveals that loss of the C-terminus of connexin43 limits microtubule plus-end capture and NaV1.5 localization at the intercalated disc. Cardiovasc. Res. 104, 371–381. 10.1093/cvr/cvu195 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

