Ghrelin Pre-treatment Attenuates Local Oxidative Stress and End Organ Damage During Cardiopulmonary Bypass in Anesthetized Rats
- PMID: 29593559
- PMCID: PMC5854848
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00196
Ghrelin Pre-treatment Attenuates Local Oxidative Stress and End Organ Damage During Cardiopulmonary Bypass in Anesthetized Rats
Abstract
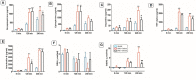
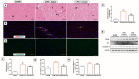
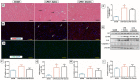
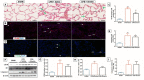
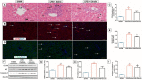
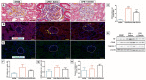
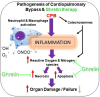
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) induced systemic inflammation significantly contributes to the development of postoperative complications, including respiratory failure, myocardial, renal and neurological dysfunction and ultimately can lead to failure of multiple organs. Ghrelin is a small endogenous peptide with wide ranging physiological effects on metabolism and cardiovascular regulation. Herein, we investigated the protective effects of ghrelin against CPB-induced inflammatory reactions, oxidative stress and acute organ damage. Adult male Sprague Dawley rats randomly received vehicle (n = 5) or a bolus of ghrelin (150 μg/kg, sc, n = 5) and were subjected to CPB for 4 h (protocol 1). In separate rats, ghrelin pre-treatment (protocol 2) was compared to two doses of ghrelin (protocol 3) before and after CPB for 2 h followed by recovery for 2 h. Blood samples were taken prior to CPB, and following CPB at 2 h and 4 h. Organ nitrosative stress (3-nitrotyrosine) was measured by Western blotting. CPB induced leukocytosis with increased plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 indicating a potent inflammatory response. Ghrelin treatment significantly reduced plasma organ damage markers (lactate dehydrogenase, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase) and protein levels of 3-nitrotyrosine, particularly in the brain, lung and liver, but only partly suppressed inflammatory cell invasion and did not reduce proinflammatory cytokine production. Ghrelin partially attenuated the CPB-induced elevation of epinephrine and to a lesser extent norepinephrine when compared to the CPB saline group, while dopamine levels were completely suppressed. Ghrelin treatment sustained plasma levels of reduced glutathione and decreased glutathione disulphide when compared to CPB saline rats. These results suggest that even though ghrelin only partially inhibited the large CPB induced increase in catecholamines and organ macrophage infiltration, it reduced oxidative stress and subsequent cell damage. Pre-treatment with ghrelin might provide an effective adjunct therapy for preventing widespread CPB induced organ injury.
Keywords: cardiopulmonary bypass; ghrelin; inflammation; organ damage; oxidative stress.
Figures
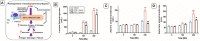
References
-
- Abdel-Salam O. M. E., Nada S. A., Salem N. A., El-Sayed El-Shamarka M., Omara E. (2013). Effect of Cannabis sativa on oxidative stress and organ damage after systemic endotoxin administration in mice. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 23, 1069–1085. 10.1007/s00580-013-1745-1 - DOI
-
- Boyle E. M., Pohlman T. H., Johnson M. C., Verrier E. D. (1997). Endothelial cell injury in cardiovascular surgery: the systemic inflammatory response. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 63, 277–284. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

