EEG Correlates of the Flow State: A Combination of Increased Frontal Theta and Moderate Frontocentral Alpha Rhythm in the Mental Arithmetic Task
- PMID: 29593605
- PMCID: PMC5855042
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00300
EEG Correlates of the Flow State: A Combination of Increased Frontal Theta and Moderate Frontocentral Alpha Rhythm in the Mental Arithmetic Task
Abstract
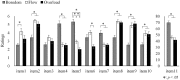
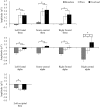
Flow experience is a subjective state experienced during holistic involvement in a certain activity, which has been reported to function as a factor promoting motivation, skill development, and better performance in the activity. To verify the positive effects of flow and develop a method to utilize it, the establishment of a reliable measurement of the flow state is essential. The present study utilized an electroencephalogram (EEG) during an experimentally evoked flow state and examined the possibility of objective measurement of immediate flow. A total of 16 participants (10 males, 6 females) participated in the experiment that employed a mental arithmetic task developed in a previous study. Post-trial self-report of the flow state and EEG during task execution were measured and compared among three conditions (Boredom, Flow, and Overload) that had different levels of task difficulty. Furthermore, the correlations between subjective flow items and EEG activity were examined. As expected, the ratings on the subjective evaluation items representing the flow state were the highest in the Flow condition. Regarding the EEG data, theta activities in the frontal areas were higher in the Flow and the Overload conditions than in the Boredom condition, and alpha activity in the frontal areas and the right central area gradually increased depending on the task difficulty. These EEG activities correlated with self-reported flow experience, especially items related to the concentration on the task and task difficulty. From the results, the flow state was characterized by increased theta activities in the frontal areas and moderate alpha activities in the frontal and central areas. The former may be related to a high level of cognitive control and immersion in task, and the latter suggests that the load on the working memory was not excessive. The findings of this study suggest the possibility of distinguishing the flow state from other states using multiple EEG activities and indicate the need for other physiological indicators corresponding to the other aspects of flow experience.
Keywords: EEG; FM theta; Flow experience; Objective measurement; mental arithmetic task.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The brain under pressure: Exploring neurophysiological responses to cognitive stress.Brain Cogn. 2024 Dec;182:106239. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2024.106239. Epub 2024 Nov 17. Brain Cogn. 2024. PMID: 39556965
-
Mental Flow Estimation Through Wearable EEG.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2022 Jul;2022:4672-4678. doi: 10.1109/EMBC48229.2022.9871594. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2022. PMID: 36086606
-
Frontal midline theta rhythm is correlated with cardiac autonomic activities during the performance of an attention demanding meditation procedure.Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2001 Apr;11(2):281-7. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6410(00)00086-0. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11275489
-
The visual scoring of sleep and arousal in infants and children.J Clin Sleep Med. 2007 Mar 15;3(2):201-40. J Clin Sleep Med. 2007. PMID: 17557427 Review.
-
Frontal-midline theta from the perspective of hippocampal "theta".Prog Neurobiol. 2008 Nov;86(3):156-85. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.09.005. Epub 2008 Sep 7. Prog Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18824212 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural Oscillation During Mental Imagery in Sport: An Olympic Sailor Case Study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Jun 1;15:669422. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.669422. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34140884 Free PMC article.
-
Can EEG Correlates Predict Treatment Efficacy in Children with Overlapping ASD and SLI Symptoms: A Case Report.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Apr 28;12(5):1110. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12051110. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626266 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-computer-interface-driven artistic expression: real-time cognitive visualization in the pangolin scales animatronic dress and screen dress.Front Hum Neurosci. 2025 Mar 6;19:1516776. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1516776. eCollection 2025. Front Hum Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40115887 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of music tempo on movement flow.Front Psychol. 2024 Jan 29;15:1292516. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1292516. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38348258 Free PMC article.
-
The Neuroscience of the Flow State: Involvement of the Locus Coeruleus Norepinephrine System.Front Psychol. 2021 Apr 14;12:645498. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.645498. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33935902 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Addessi A. R., Ferrari L., Carugati F. (2015). The flow grid: a technique for observing and measuring emotional state in children interacting with a flow machine. J. New. Music. Res. 44, 129–144. 10.1080/09298215.2014.991738 - DOI
-
- Bakker A. B. (2005). Flow among music teachers and their students: the crossover of peak experiences. J. Vocat. Behav. 66, 26–44. 10.1016/j.jvb.2003.11.001 - DOI
-
- Biasutti M. (2017). Flow and optimal experience, in Reference Module in Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Psychology, ed Stein J. P. (New York, NY: Elsevier; ), 522–528.
-
- Carli M., Fave A. D., Massimini F. (1988). The Quality of Experience in the Flow Channels: Comparison of Italian and US students. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

