The Educational Situation Quality Model: Recent Advances
- PMID: 29593623
- PMCID: PMC5861203
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00328
The Educational Situation Quality Model: Recent Advances
Abstract
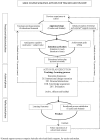
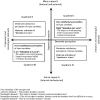
The purpose of this work was to present an educational model developed in recent years entitled the "The Educational Situation Quality Model" (MOCSE, acronym in Spanish). MOCSE can be defined as an instructional model that simultaneously considers the teaching-learning process, where motivation plays a central role. It explains the functioning of an educational setting by organizing and relating the most important variables which, according to the literature, contribute to student learning. Besides being a conceptual framework, this model also provides a methodological procedure to guide research and to promote reflection in the classroom. It allows teachers to implement effective research-action programs to improve teacher-students satisfaction and learning outcomes in the classroom context. This work explains the model's characteristics and functioning, recent advances, and how teachers can use it in an educational setting with a specific subject. This proposal integrates approaches from several relevant psycho-educational theories and introduces a new perspective into the existing literature that will allow researchers to make progress in studying educational setting functioning. The initial MOCSE configuration has been refined over time in accordance with the empirical results obtained from previous research, carried out within the MOCSE framework and with the subsequent reflections that derived from these results. Finally, the contribution of the model to improve learning outcomes and satisfaction, and its applicability in the classroom, are also discussed.
Keywords: educational model; formative evaluation; learning outcomes; research in the classroom; teaching–learning process.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of Teacher and Family Support on University Student Motivation and Engagement.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 5;18(5):2606. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052606. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33807813 Free PMC article.
-
The Educational Situation Quality Model: A New Tool to Explain and Improve Academic Achievement and Course Satisfaction.Front Psychol. 2019 Jul 18;10:1692. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01692. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31379696 Free PMC article.
-
MOCSE Centered on Students: Validation of Learning Demands and Teacher Support Scales.Front Psychol. 2020 Oct 2;11:582926. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.582926. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 33117247 Free PMC article.
-
A Conceptual Review of Positive Teacher Interpersonal Communication Behaviors in the Instructional Context.Front Psychol. 2021 Jul 15;12:708490. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.708490. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34335424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of flipped classrooms to improve learning outcomes in undergraduate health professional education: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 7;19(3):e1339. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1339. eCollection 2023 Sep. Campbell Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37425620 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Dynamic Analysis of the Asymmetric Effects of the Vocational Education and Training on Economic Growth, Evidence From China.Front Psychol. 2022 May 23;13:888969. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.888969. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. Retraction in: Front Psychol. 2023 Dec 12;14:1345809. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1345809. PMID: 35677120 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Influence of Teacher and Family Support on University Student Motivation and Engagement.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 5;18(5):2606. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052606. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33807813 Free PMC article.
-
Criteria for Teaching Performance in Psychology: Invariance According to Age, Sex, and Academic Stage of Peruvian Students.Front Psychol. 2021 Oct 26;12:764081. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.764081. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34777170 Free PMC article.
-
The Educational Situation Quality Model: A New Tool to Explain and Improve Academic Achievement and Course Satisfaction.Front Psychol. 2019 Jul 18;10:1692. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01692. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31379696 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Curricular Reform in Medical Schools and the Ship of Theseus: Insights Regarding Philosophical and Ideological Characteristics.Med Sci Educ. 2019 Apr 9;29(2):599-602. doi: 10.1007/s40670-019-00726-0. eCollection 2019 Jun. Med Sci Educ. 2019. PMID: 34457518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abellán L. (2016). Motivación y Aprendizaje Escolar en la Educación Secundaria Obligatoria: Un Estudio Empírico Desde el Modelo de Calidad de Situación Educativa [Scholar Learning and Motivation: Un Empirical Study from the Quality Educational Setting Model]. Doctoral dissertation, University of Valencia; Valencia.
-
- Alonso Tapia J. (2002). Motivación y Aprendizaje en el Aula. Cómo Enseñar a Pensar. Madrid: Editorial Santillana.
-
- Ames C. (1992). Classrooms: goals, structures, and student motivation. J. Educ. Psychol. 84 261–271. 10.1037/0022-0663.84.3.261 - DOI
-
- Bakker A. B., Demerouti E. (2007). The job demands resources model: state of the art. J. Manag. Psychol. 22 309–328. 10.1108/02683940710733115 - DOI
-
- Bandura A. (1987). Pensamiento y Acción. Fundamentos Sociales. Barcelona: Martínez Roca.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

