11β-HSD Types 1 and 2 in the Songbird Brain
- PMID: 29593652
- PMCID: PMC5857549
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00086
11β-HSD Types 1 and 2 in the Songbird Brain
Abstract
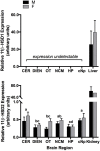
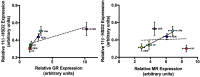
Glucocorticoid (GC) hormones act on the brain to regulate diverse functions, from behavior and homeostasis to the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Local regeneration and metabolism of GCs can occur in target tissues through the actions of the 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases [11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11β-HSD1) and 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (11β-HSD2), respectively] to regulate access to GC receptors. Songbirds have become especially important model organisms for studies of stress hormone action; however, there has been little focus on neural GC metabolism. Therefore, we tested the hypothesis that 11β-HSD1 and 11β-HSD2 are expressed in GC-sensitive regions of the songbird brain. Localization of 11β-HSD expression in these regions could provide precise temporal and spatial control over GC actions. We quantified GC sensitivity in zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata) brain by measuring glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) expression across six regions, followed by quantification of 11β-HSD1 and 11β-HSD2 expression. We detected GR, MR, and 11β-HSD2 mRNA expression throughout the adult brain. Whereas 11β-HSD1 expression was undetectable in the adult brain, we detected low levels of expression in the brain of developing finches. Across several adult brain regions, expression of 11β-HSD2 covaried with GR and MR, with the exception of the cerebellum and hippocampus. It is possible that receptors in these latter two regions require direct access to systemic GC levels. Overall, these results suggest that 11β-HSD2 expression protects the adult songbird brain by rapid metabolism of GCs in a context and region-specific manner.
Keywords: 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; glucocorticoid; mineralocorticoid; songbird; stress response.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Distinct ontogeny of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor and 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase types I and II mRNAs in the fetal rat brain suggest a complex control of glucocorticoid actions.J Neurosci. 1998 Apr 1;18(7):2570-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-07-02570.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9502816 Free PMC article.
-
11ß hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases regulate circulating glucocorticoids but not central gene expression.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2021 May 1;305:113734. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2021.113734. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33548254 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial and temporal patterns of expression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase types 1 and 2 messenger RNA and glucocorticoid receptor protein in the murine placenta and uterus during late pregnancy.Biol Reprod. 2002 Dec;67(6):1708-18. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.102.005488. Biol Reprod. 2002. PMID: 12444044
-
Getting to the heart of intracellular glucocorticoid regeneration: 11β-HSD1 in the myocardium.J Mol Endocrinol. 2017 Jan;58(1):R1-R13. doi: 10.1530/JME-16-0128. Epub 2016 Aug 23. J Mol Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27553202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
11beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the brain: a novel regulator of glucocorticoid action?Front Neuroendocrinol. 1997 Jan;18(1):49-99. doi: 10.1006/frne.1996.0143. Front Neuroendocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9000459 Review.
Cited by
-
The stressed brain: regional and stress-related corticosterone and stress-regulated gene expression in the adult zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata).J Neuroendocrinol. 2020 May;32(5):e12852. doi: 10.1111/jne.12852. Epub 2020 May 4. J Neuroendocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32364267 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Maternal Chewing on Prenatal Stress-Induced Cognitive Impairments in the Offspring via Multiple Molecular Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 6;21(16):5627. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165627. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32781547 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of 11-dehydrocorticosterone in mice, rats and songbirds: Effects of age, sex and stress.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2019 Sep 15;281:173-182. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2019.05.018. Epub 2019 May 27. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31145891 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonally sympatric but allochronic: differential expression of hypothalamic genes in a songbird during gonadal development.Proc Biol Sci. 2018 Oct 24;285(1889):20181735. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2018.1735. Proc Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30355713 Free PMC article.
-
Preparing to migrate: expression of androgen signaling molecules and insulin-like growth factor-1 in skeletal muscles of Gambel's white-crowned sparrows.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2019 Feb;205(1):113-123. doi: 10.1007/s00359-018-1308-7. Epub 2018 Dec 8. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30535830
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

