Age-related differences in function and structure of rat livers subjected to ischemia/reperfusion
- PMID: 29593814
- PMCID: PMC5868678
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2018.73470
Age-related differences in function and structure of rat livers subjected to ischemia/reperfusion
Abstract
Introduction: Liver function is affected during ischemia/reperfusion (IR). The current state of knowledge about liver aging processes during IR is incomplete. We evaluated the effects of aging on liver structure and function under IR conditions.
Material and methods: Animals were divided into control (C-2) and ischemia/reperfusion (IR-2) groups of young rats (2-4 months old) and C-12 and IR-12 groups of old rats (12-14 months old). The livers from IR-2 and IR-12 groups were subjected to partial ischemia (60 min), followed by global reperfusion (4 h). Blood samples were obtained during reperfusion (0, 30 and 240 min) to estimate the activity of aminotransferases (ALT, AST). After IR, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1b (IL-1b), malondialdehyde (MDA), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were determined in liver homogenates.
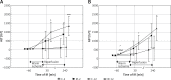
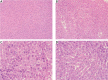
Results: At all points of reperfusion, an increase in aminotransferase activity levels in the ischemic groups was observed; mainly between IR-12 and C-12 rats. The concentration of TNF-α was significantly higher in young animals (in non-ischemic groups: p = 0.09, in ischemic groups: p = 0.05). Under IR conditions, the concentration of IL-1b dropped (p = 0.05). The concentration of MDA was significantly higher in mature animals (in non-ischemic groups: p = 0.09, in ischemic groups: p = 0.05). In ischemic groups an increase in necrosis rate was observed regardless of age. Rats in the IR-12 group showed the most pronounced changes in hepatic architecture, including increased micro- and macrosteatosis and parenchymal cell destruction.
Conclusions: The function and structure of mature livers slightly deteriorate with age and these differences are more noticeable under IR conditions.
Keywords: ageing; inflammation; ischemia/reperfusion; liver; oxidative stress; rat.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Age-related changes in ADMA-DDAH-NO pathway in rat liver subjected to partial ischemia followed by global reperfusion.Exp Gerontol. 2014 Feb;50:45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Exp Gerontol. 2014. PMID: 24269305
-
Liraglutide attenuates partial warm ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat livers.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;390(3):311-319. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1330-7. Epub 2016 Dec 16. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27986979
-
Sitagliptin-Dependent Differences in the Intensity of Oxidative Stress in Rat Livers Subjected to Ischemia and Reperfusion.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Oct 31;2019:2738605. doi: 10.1155/2019/2738605. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31781329 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects of different-time-ischemic preconditioning on the reperfusion injury in fatty livers in rats.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058086. Epub 2013 Mar 6. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23483973 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of low doses of tumor necrosis factor-alpha protects rat liver from ischaemic damage and reperfusion injury.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;61(3):273-8. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20610856
Cited by
-
Acute liver failure secondary to toxic exposure in children.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Sep 9;18(1):84-91. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.87716. eCollection 2022. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 35154529 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of benfotiamine on irisin activity in methotrexate-induced liver injury in rats.Arch Med Sci. 2018 Nov 29;16(1):205-211. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2018.80002. eCollection 2020. Arch Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 32051725 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA 144 inhibits cell migration and invasion and regulates inflammatory cytokine secretion through targeting toll like receptor 2 in non-small cell lung cancer.Arch Med Sci. 2020 Mar 10;17(4):1028-1037. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2020.93084. eCollection 2021. Arch Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 34336030 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress, immunological and cellular hypoxia biomarkers in hepatitis C treatment-naïve and cirrhotic patients.Arch Med Sci. 2020 Jan 3;17(2):368-375. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.91451. eCollection 2021. Arch Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33747272 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphism and antioxidant activity in interventions of tobacco-related diseases of the abdominal aorta.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Aug 7;18(4):1071-1077. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.86760. eCollection 2022. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 35832719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cobreros A, Sainz L, Lasheras B, Cenarruzabeitia E. Hepatotoxicity of ethanol: protective effect of calcium channel blockers in isolated hepatocytes. Liver. 1997;17:76–82. - PubMed
-
- Fan C, Zwacka RM, Engelhardt JF. Therapeutic approaches for ischemia/reperfusion injury in the liver. J Mol Med. 1999;77:577–96. - PubMed
-
- Hines IN, Harada H, Flores S, Gao B, McCord JM, Grisham MB. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase protects the post-ischemic liver: potential interactions with superoxide. Biomed Pharmacother. 2005;59:183–9. - PubMed
-
- Peralta C, Fernández L, Panés J, et al. Preconditioning protects against systemic disorders associated with hepatic ischemia-reperfusion through blockade of tumor necrosis factor-induced P-selectin up-regulation in the rat. Hepatology. 2001;33:100–13. - PubMed
-
- Perry BC, Soltys D, Toledo AH, Toledo-Pereyra LF. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Invest Surg. 2011;24:178–88. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
