Preventive effects of total saponins of Panax japonicus on fatty liver fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 29593815
- PMCID: PMC5868672
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2016.63260
Preventive effects of total saponins of Panax japonicus on fatty liver fibrosis in mice
Abstract
Introduction: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition in which excess fat accumulates in the liver of a patient without a history of alcohol abuse. Fatty liver fibrosis, a severe form of NAFLD, is a key step which can be reversed by effective medical intervention. This paper aims to describe the protective role and mechanisms of action of total saponins of Panax japonicus (SPJ) against fatty liver fibrosis in mice. In this study, fatty liver fibrosis was induced by a high-fat (HF) diet combined with intraperitoneal injection of porcine serum.
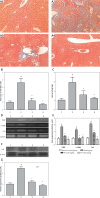
Material and methods: The fatty liver fibrosis model was induced by HF diet combined with intraperitoneal injection of porcine serum. The endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) response and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and p-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-mediated apoptosis and inflammation were assessed by serum biochemistry, hematoxylin-eosin (H + E), Masson and electronic microscopy staining, Hyp content detection, Western blotting and real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
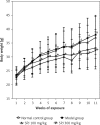
Results: Saponins of Panax japonicus could significantly improve liver function and decrease the lipid level in the serum. The liver steatosis, collagen fibers and inflammatory cell infiltration were significantly improved in the SPJ group according to microscope observation. The RT-PCR analysis revealed that the collagen I (Coll), α smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), tissue inhibitors of MMPs (TIMP), CHOP and GRP78 mRNA expression levels were distinctly weakened by SPJ treatment; and western blotting analysis indicated that the phosphorylated JNK (p-JNK), Coll and 78 kD glucose-regulated protein (GRP78) protein expression levels were significantly alleviated, which might be associated with the inhibition of the ERS response and the CHOP and JNK-mediated apoptosis and inflammation pathway.
Conclusions: Based on this research, SPJ as a preventive medicine has great potential in prevention of liver fibrosis.
Keywords: Coll; JNK; endoplasmic reticulum stress; fatty liver fibrosis; total saponins of Panax japonicus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Dyson J, Day C. Treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis. 2014;32:597–604. - PubMed
-
- Balunas MJ, Kinghorn AD. Drug discovery from medicinal plants. Life Sci. 2005;78:431–41. - PubMed
-
- He YM, Lu KM, Yuan D, Zhang CC. Studies on preparative technology and quantitative determination for extracts of total saponin in roof of Panax japonicus. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008;33:2607–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
