Hybrid Assistive Limb Intervention in a Patient with Late Neurological Deterioration after Thoracic Myelopathy Surgery due to Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum
- PMID: 29593925
- PMCID: PMC5822893
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6171760
Hybrid Assistive Limb Intervention in a Patient with Late Neurological Deterioration after Thoracic Myelopathy Surgery due to Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum
Abstract
Purpose: We evaluated improvements in gait after using the Hybrid Assistive Limb (HAL®) exoskeleton robot in a patient with late-onset neurological deterioration of lower extremity function after undergoing thoracic spine surgery for a myelopathy due to ossification of the ligamentum flavum.
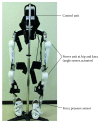
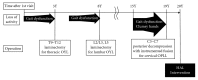
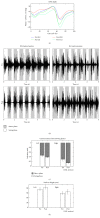
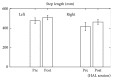
Case presentation: A 70-year-old man participated in ten 20 min sessions of HAL intervention, twice weekly for five weeks. The effects of each HAL session were evaluated based on changes in performance on the 10 m walk test (10 MWT), lower limb kinematics quantified from motion capture, and the activation ratio of the gastrocnemius, measured before and after the intervention. Muscle activity was recorded using surface electromyography and synchronized to measured kinematics. The HAL intervention improved gait speed and step length, with an increase in the hip flexion angle during the swing phase and a decrease in the activation ratio of the gastrocnemius. The modified Ashworth scale improved from 1+ to 1 and International Standards for Neurological and Functional Classification of Spinal Cord Injury motor scores from 34 to 49.
Conclusion: Intervention using the HAL exoskeleton robot may be an effective method to improve functional ambulation in patients with chronic spinal disorders.
Figures





References
-
- Kawamoto H., Sankai Y. Power assist method based on phase sequence and muscle force condition for HAL. Advanced Robotics. 2005;19(7):717–734. doi: 10.1163/1568553054455103. - DOI
-
- Colombo G., Joerg M., Schreier R., Dietz V. Treadmill training of paraplegic patients using a robotic orthosis. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development. 2000;37(6):693–700. - PubMed
-
- Veneman J. F., Kruidhof R., Hekman E. E. G., Ekkelenkamp R., Van Asseldonkand E. H. F., van der Kooij H. Design and evaluation of the LOPES exoskeleton robot for interactive gait rehabilitation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering. 2007;15(3):379–86. doi: 10.1109/tnsre.2007.903919. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

