Stopping screening, when and how?
- PMID: 29594019
- PMCID: PMC5861277
- DOI: 10.21037/tau.2017.12.39
Stopping screening, when and how?
Abstract
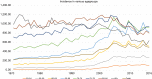
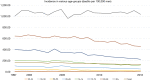
Screening for prostate cancer (PC) is still controversial despite randomized trials has found that PC mortality is decreased. The major concern is the high rate of over-diagnosis and subsequent harms that may follow in many men who never would have had any symptoms during life-time if not screened. The high rate of over-diagnosis is driven by the large reservoir of small non-significant cancers that increases with age and found in more than half of men over 70 years, the low specificity of prostate specific antigen (PSA) but also by current "blind" biopsy technique that risk accidentally to hit these small non-significant cancers. The risk of over-diagnosis is increasing with age and the trade-off by screening men in high age is probably higher. At what age harms exceeds benefits is not established but modelling studies has demonstrated that after 65-70 years the quality adjusted life-years (QALYs) gained are decreasing but still on the positive side if screening is continued up to 75 years. A dilemma is that most PC deaths occur in men after the age 80 and the effect of screening seems not to last as long as was thought, already 10 years after termination of screening PC mortality has caught up in the screening arm to a level similar to that in the control group. In the European Randomised Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer (ERSPC) screening was terminated between 71 and 75 years and the first effect of screening on mortality was discernible after 7 years and has been relatively stable around 20% since 9 years after study start. It seems questionable from any standpoint to invite men for screening with an expected life length below 10 years, which is the expected life-length of an averaged 78-year-old man in 2018. However, the balance between harms and benefits specifically in the age 70-80 need more attention as also costs need. Permanent side-effects from (unnecessary) treatments and their impact on quality of life must be evaluated better and related to age and individual variations. In future better screening methods with more specific markers and introduction of imaging will hopefully decrease the present large risk of over-diagnosis in elderly men and thereby expand efficient screening to men in the age group >70 who actually is the high risk group of dying from PC.
Keywords: Prostate cancer (PC); age; epidemiology; over-diagnosis; screening.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Nordstrom T, Aly M, Clements MS, et al. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing is prevalent and increasing in Stockholm County, Sweden, Despite no recommendations for PSA screening: results from a population-based study, 2003-2011. Eur Urol 2013;63:419-25. 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.10.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous