The response to DNA damage in heterochromatin domains
- PMID: 29594515
- PMCID: PMC6440646
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-018-0669-6
The response to DNA damage in heterochromatin domains
Abstract
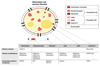
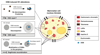
Eukaryotic genomes are organized into chromatin, divided into structurally and functionally distinct euchromatin and heterochromatin compartments. The high level of compaction and the abundance of repeated sequences in heterochromatin pose multiple challenges for the maintenance of genome stability. Cells have evolved sophisticated and highly controlled mechanisms to overcome these constraints. Here, we summarize recent findings on how the heterochromatic state influences DNA damage formation, signaling, and repair. By focusing on distinct heterochromatin domains in different eukaryotic species, we highlight the heterochromatin contribution to the compartmentalization of DNA damage repair in the cell nucleus and to the repair pathway choice. We also describe the diverse chromatin alterations associated with the DNA damage response in heterochromatin domains and present our current understanding of their regulatory mechanisms. Finally, we discuss the biological significance and the evolutionary conservation of these processes.
Keywords: Chromatin reorganization; DNA damage repair; Heterochromatin; Nuclear domains.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

