Refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia with concomitant acute cerebral infarction in a child: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 29595632
- PMCID: PMC5895422
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010103
Refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia with concomitant acute cerebral infarction in a child: A case report and literature review
Abstract
Rationale: Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia, a common cause of community-acquired pneumonia in children, is rarely complicated with acute cerebral infarction.
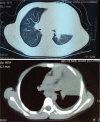
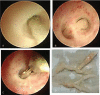
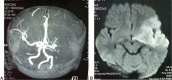
Patient concerns: We present a 7-year-old boy with severe M pneumoniae pneumonia who developed impaired consciousness, aphasia, and reduced limb muscle power 7 days postadmission.
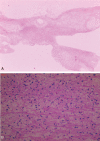
Diagnoses: Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia with concomitant acute cerebral infarction.
Interventions: The patient recovered with aggressive antibiotic therapy, antiinflammation therapy with methylprednisolone, and gamma immunoglobulin and anticoagulation therapy with aspirin and low molecular weight heparin along with rehabilitation training.
Outcomes: At 8 days postadmission, his consciousness was improved and at the 6-month follow-up visit, his muscle power of bilateral upper and lower limbs was normal except still poor right handgrip power.
Lessons: Stroke or cerebral infarction should be considered and promptly managed in rare cases of M pneumoniae pneumonia with neurologic manifestations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Rogozinski LE, Alverson BK, Biondi EA. Diagnosis and treatment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children. Minerva Pediatr 2017;69:156–60. - PubMed
-
- Meyer Sauteur PM, et al. Severe childhood Guillain-Barre syndrome associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: a case series. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2015;20:72–8. - PubMed
-
- Candler PM, Dale RC. Three cases of central nervous system complications associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Pediatr Neurol 2004;31:133–8. - PubMed
-
- Schoenberg BS, Mellinger JF, Schoenberg DG. Cerebrovascular disease in infants and children: a study of incidence, clinical features, and survival. Neurology 1978;28:763–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

