Taking a bite out of nutrition and arbovirus infection
- PMID: 29596427
- PMCID: PMC5875747
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006247
Taking a bite out of nutrition and arbovirus infection
Abstract
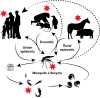
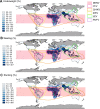
Nutrition is a key factor in host-pathogen defense. Malnutrition can increase both host susceptibility and severity of infection through a number of pathways, and infection itself can promote nutritional deterioration and further susceptibility. Nutritional status can also strongly influence response to vaccination or therapeutic pharmaceuticals. Arthropod-borne viruses (arboviruses) have a long history of infecting humans, resulting in regular pandemics as well as an increasing frequency of autochthonous transmission. Interestingly, aside from host-related factors, nutrition could also play a role in the competence of vectors required for transmission of these viruses. Nutritional status of the host and vector could even influence viral evolution itself. Therefore, it is vital to understand the role of nutrition in the arbovirus lifecycle. This Review will focus on nutritional factors that could influence susceptibility and severity of infection in the host, response to prophylactic and therapeutic strategies, vector competence, and viral evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Katona P, Katona-Apte J. The Interaction between Nutrition and Infection. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2008;46(10):1582–8. doi: 10.1086/587658 - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Fact Sheet 311: Obesity 2016 [cited 2017 July 31]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/.
-
- World Health Organization. Fact sheet: Malnutrition 2017 [cited 2017 31 July]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/malnutrition/en/.
-
- Chapman IM. Nutritional Disorders in the Elderly. Medical Clinics of North America. 2006;90(5):887–907. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2006.05.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Disease Control Priorities Project. Eliminating Malnutrition Could Reduce Poor Countries’ Disease Burden by One-Third. 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

