Age-related collagen turnover of the interstitial matrix and basement membrane: Implications of age- and sex-dependent remodeling of the extracellular matrix
- PMID: 29596429
- PMCID: PMC5875766
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194458
Age-related collagen turnover of the interstitial matrix and basement membrane: Implications of age- and sex-dependent remodeling of the extracellular matrix
Abstract
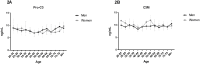
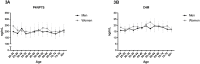
The extracellular matrix (ECM) plays a vital role in maintaining normal tissue function. Collagens are major components of the ECM and there is a tight equilibrium between degradation and formation of these proteins ensuring tissue health and homeostasis. As a consequence of tissue turnover, small collagen fragments are released into the circulation, which act as important biomarkers in the study of certain tissue-related remodeling factors in health and disease. The aim of this study was to establish an age-related collagen turnover profile of the main collagens of the interstitial matrix (type I and III collagen) and basement membrane (type IV collagen) in healthy men and women. By using well-characterized competitive ELISA-assays, we assessed specific fragments of degraded (C1M, C3M, C4M) and formed (PINP, Pro-C3, P4NP7S) type I, III and IV collagen in serum from 617 healthy men and women ranging in ages from 22 to 86. Subjects were divided into 5-year age groups according to their sex and age. Groups were compared using Kruskal-Wallis adjusted for Dunn's multiple comparisons test and Mann-Whitney t-test. Age-specific changes in collagen turnover was most profound for type I collagen. PINP levels decreased in men with advancing age, whereas in women, the level decreased in early adulthood followed by an increase around the age of menopause (age 40-60). Sex-specific changes in type I, III and IV collagen turnover was present at the age around menopause (age 40-60) with women having an increased turnover. In summary, collagen turnover is affected by age and sex with the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane being differently regulated. The observed changes needs to be accounted for when measuring ECM related biomarkers in clinical studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
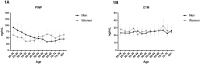
Similar articles
-
Fibrosis is not just fibrosis - basement membrane modelling and collagen metabolism differs between hepatitis B- and C-induced injury.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Dec;44(11-12):1242-1252. doi: 10.1111/apt.13819. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27696451
-
The collagen turnover profile is altered in patients with inguinal and incisional hernia.Surgery. 2015 Feb;157(2):312-21. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2014.09.006. Surgery. 2015. PMID: 25616945
-
Extracellular Matrix Fragments of the Basement Membrane and the Interstitial Matrix Are Serological Markers of Intestinal Tissue Remodeling and Disease Activity in Dextran Sulfate Sodium Colitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Nov;64(11):3134-3142. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05676-6. Epub 2019 May 24. Dig Dis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31123972
-
Fibrillar, fibril-associated and basement membrane collagens of the arterial wall: architecture, elasticity and remodeling under stress.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(9):1124-33. doi: 10.2174/1381612820666141013122906. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 25312736 Review.
-
The borderline: basement membranes and the transition from premalignant to malignant neoplasia.Microsc Res Tech. 1994 Jun 15;28(3):216-25. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070280306. Microsc Res Tech. 1994. PMID: 8068984 Review.
Cited by
-
Revisiting Circulating Extracellular Matrix Fragments as Disease Markers in Myelofibrosis and Related Neoplasms.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;15(17):4323. doi: 10.3390/cancers15174323. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37686599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium‑sensing receptor promotes high glucose‑induced myocardial fibrosis via upregulation of the TGF‑β1/Smads pathway in cardiac fibroblasts.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Aug;20(2):1093-1102. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10330. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31173208 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Parainflammation in Chronic Glaucoma Using Vitreous-OCT Imaging.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 29;9(12):1792. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121792. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34944608 Free PMC article.
-
Serological assessment of collagen fragments and tumor fibrosis may guide immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Oct 16;40(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02133-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34656158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collagen mimetic peptides as novel therapeutics for vascular disease in the central nervous system.Front Neurosci. 2025 May 12;19:1569347. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1569347. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40421131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yurchenco PD, Schittny JC. Molecular architecture of basement membranes. FASEB J [Internet]. 1990;4(6):1577–90. Available from: http://www.fasebj.org/content/4/6/1577.short%5Cnhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.... - PubMed
-
- Bosman FT, Stamenkovic I. Functional structure and composition of the extracellular matrix. J Pathol [Internet]. 2003;200(4):423–8. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12845610%5Cnhttp://doi.wiley.com/10.1... - DOI - PubMed
-
- Karsdal MA, Genovese F, Madsen EA, Manon-Jensen T, Schuppan D. Collagen and tissue turnover as a function of age: Implications for fibrosis. J Hepatol. 2016;64(1):103–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.014 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frantz C, Stewart KM, Weaver VM. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci [Internet]. 2010;123(24):4195–200. Available from: http://jcs.biologists.org/cgi/doi/10.1242/jcs.023820 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karsdal MA, Nielsen MJ, Sand JM, Henriksen K, Genovese F, Bay-Jensen AC, et al. Extracellular matrix remodeling: the common denominator in connective tissue diseases. Possibilities for evaluation and current understanding of the matrix as more than a passive architecture, but a key player in tissue failure. Vol. 11, Assay.Drug Dev.Technol. p. 70–92. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

