Manual muscle testing and hand-held dynamometry in people with inflammatory myopathy: An intra- and interrater reliability and validity study
- PMID: 29596450
- PMCID: PMC5875759
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194531
Manual muscle testing and hand-held dynamometry in people with inflammatory myopathy: An intra- and interrater reliability and validity study
Abstract
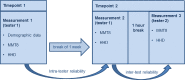
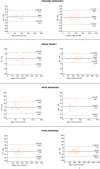
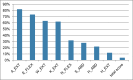
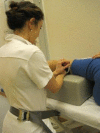
Manual muscle testing (MMT) and hand-held dynamometry (HHD) are commonly used in people with inflammatory myopathy (IM), but their clinimetric properties have not yet been sufficiently studied. To evaluate the reliability and validity of MMT and HHD, maximum isometric strength was measured in eight muscle groups across three measurement events. To evaluate reliability of HHD, intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC), the standard error of measurements (SEM) and smallest detectable changes (SDC) were calculated. To measure reliability of MMT linear Cohen`s Kappa was computed for single muscle groups and ICC for total score. Additionally, correlations between MMT8 and HHD were evaluated with Spearman Correlation Coefficients. Fifty people with myositis (56±14 years, 76% female) were included in the study. Intra-and interrater reliability of HHD yielded excellent ICCs (0.75-0.97) for all muscle groups, except for interrater reliability of ankle extension (0.61). The corresponding SEMs% ranged from 8 to 28% and the SDCs% from 23 to 65%. MMT8 total score revealed excellent intra-and interrater reliability (ICC>0.9). Intrarater reliability of single muscle groups was substantial for shoulder and hip abduction, elbow and neck flexion, and hip extension (0.64-0.69); moderate for wrist (0.53) and knee extension (0.49) and fair for ankle extension (0.35). Interrater reliability was moderate for neck flexion (0.54) and hip abduction (0.44); fair for shoulder abduction, elbow flexion, wrist and ankle extension (0.20-0.33); and slight for knee extension (0.08). Correlations between the two tests were low for wrist, knee, ankle, and hip extension; moderate for elbow flexion, neck flexion and hip abduction; and good for shoulder abduction. In conclusion, the MMT8 total score is a reliable assessment to consider general muscle weakness in people with myositis but not for single muscle groups. In contrast, our results confirm that HHD can be recommended to evaluate strength of single muscle groups.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Greenberg SA. Inflammatory myopathies: evaluation and management. Semin Neurol. 2008;28(2):241–9. Epub 2008/03/21. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1062267 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dalakas MC. Polymyositis, dermatomyositis and inclusion-body myositis. N Engl J Med. 1991;325(21):1487–98. Epub 1991/11/21. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199111213252107 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975;292(8):403–7. Epub 1975/02/20. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502202920807 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rider LG, Koziol D, Giannini EH, Jain MS, Smith MR, Whitney-Mahoney K, et al. Validation of manual muscle testing and a subset of eight muscles for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010;62(4):465–72. Epub 2010/04/15. doi: 10.1002/acr.20035 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2924143. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rider LG, Werth VP, Huber AM, Alexanderson H, Rao AP, Ruperto N, et al. Measures of adult and juvenile dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and inclusion body myositis: Physician and Patient/Parent Global Activity, Manual Muscle Testing (MMT), Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ)/Childhood Health Assessment Questionnaire (C-HAQ), Childhood Myositis Assessment Scale (CMAS), Myositis Disease Activity Assessment Tool (MDAAT), Disease Activity Score (DAS), Short Form 36 (SF-36), Child Health Questionnaire (CHQ), physician global damage, Myositis Damage Index (MDI), Quantitative Muscle Testing (QMT), Myositis Functional Index-2 (FI-2), Myositis Activities Profile (MAP), Inclusion Body Myositis Functional Rating Scale (IBMFRS), Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), Cutaneous Assessment Tool (CAT), Dermatomyositis Skin Severity Index (DSSI), Skindex, and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63 Suppl 11:S118–57. Epub 2012/05/25. doi: 10.1002/acr.20532 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

