Self-reported cheating among medical students: An alarming finding in a cross-sectional study from Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 29596538
- PMCID: PMC5875787
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194963
Self-reported cheating among medical students: An alarming finding in a cross-sectional study from Saudi Arabia
Erratum in
-
Correction: Self-reported cheating among medical students: An alarming finding in a cross-sectional study from Saudi Arabia.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 18;14(4):e0215862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215862. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30998748 Free PMC article.
Abstract
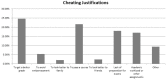
Academic misconduct/dishonesty has become widespread behavior among many university students across the globe, and medical education is not an exception. Until recently, few efforts have been made to study the dishonest behavior in Middle-Eastern universities. This study examined the prevalence and predisposing factors of cheating among medical students in Saudi Arabia and suggests suitable preventive measures. A cross-sectional survey-based study was conducted at a government medical college during the 2014-2015 academic year. The response rate was 58.5% (421/720). The overall cheating behavior practiced by the participants was 29%, predominantly by male students. High GPA scoring students were the least likely to cheat. The participants living with their families were more likely to cheat compared to those who were living apart from their families. The reasons participants gave to justify their cheating behavior included getting better grades, passing the course, and lacking preparation while still recognizing that cheating is a 'mistake.' Overall, significant academic misconduct concerning cheating was found among the Saudi medical students; this misconduct is alarming in a reputable government institution. The implementation of strict punishments, requiring ethical courses and creating ethical awareness by exploiting the potential of Islamic religious belief might help to control this problem.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reasons for academic cheating in a cohort of nursing students in Saudi Arabia: a cross-sectional study.J Med Life. 2024 Apr;17(4):418-425. doi: 10.25122/jml-2023-0517. J Med Life. 2024. PMID: 39071511 Free PMC article.
-
Croatian medical students see academic dishonesty as an acceptable behaviour: a cross-sectional multicampus study.J Med Ethics. 2012 Jun;38(6):376-9. doi: 10.1136/medethics-2011-100015. Epub 2012 Jan 12. J Med Ethics. 2012. PMID: 22240586
-
Who would students ask for help in academic cheating? Cross-sectional study of medical students in Croatia.BMC Med Educ. 2014 Dec 30;14:1048. doi: 10.1186/s12909-014-0277-y. BMC Med Educ. 2014. PMID: 25547735 Free PMC article.
-
Cheating in medical school: the unacknowledged ailment.South Med J. 2013 Aug;106(8):479-83. doi: 10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3182a14388. South Med J. 2013. PMID: 23912144 Review.
-
Why Students Cheat and How Understanding This Can Help Reduce the Frequency of Academic Misconduct in Higher Education: A Literature Review.J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2022 Jun 1;20(2):A150-A160. doi: 10.59390/LXMJ2920. eCollection 2022 Winter. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2022. PMID: 38323052 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Promoting anti-corruption, transparency and accountability in the recruitment and promotion of health workers to safeguard health outcomes.Glob Health Action. 2020;13(sup1):1701326. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2019.1701326. Glob Health Action. 2020. PMID: 32194012 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the academic misconduct questionnaire: exploring predictors of student misconduct.Med Educ Online. 2025 Dec;30(1):2506739. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2025.2506739. Epub 2025 May 23. Med Educ Online. 2025. PMID: 40405706 Free PMC article.
-
Nursing Students' Perspectives on Academic Dishonesty During Examinations and Assignments: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2024 Jan 17;16(1):e52418. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52418. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38371104 Free PMC article.
-
Reasons for academic cheating in a cohort of nursing students in Saudi Arabia: a cross-sectional study.J Med Life. 2024 Apr;17(4):418-425. doi: 10.25122/jml-2023-0517. J Med Life. 2024. PMID: 39071511 Free PMC article.
-
Are surface and deep learning approaches associated with study patterns and choices among medical students? A cross-sectional study.Sao Paulo Med J. 2018 Sep-Oct;136(5):414-420. doi: 10.1590/1516-3180.2018.0200060818. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Sao Paulo Med J. 2018. PMID: 30365597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McCabe D. Cheating among college and university students: a North American perspective. Int J Educ Integrity 2005; 1(1).
-
- Park EJ, Park S, Jang IS. Clinical misconduct among South Korean nursing students. Nurse Educ Today 2014; 34(12): 1467–1473. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2014.04.006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Agud JL. Fraud and plagiarism in school and career. Rev Clin Esp 2014; 214(7): 410–414. doi: 10.1016/j.rce.2014.03.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Muhney KA, Gutmann ME, Schneiderman E, DeWald JP, McCann A, Campbell PR. Prevalence of academic dishonesty in Texas Dental Hygiene Programs. Journal of Dental Hygiene 2008; 72(11): 1247–60. - PubMed
-
- Hrabak M, Vujaklija A, Vodopivec I, Hren D, Marusić M, Marusić A. Academic misconduct among medical students in a post-communist country. Med Educ. 2004; 38(3):276–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources